

The Cardiac Center

Before we begin our study of how the heart functions, it is important that you have a clear image of what the human heart looks like. The picture below should be helpful in identifying the external structures of the heart. For a detailed look at the internal structures of the heart, click here.

HEARTPOINT provides a wealth of material about keeping your heart and arteries healthy. Current research in cardiac care is also featured on this site.
Maybe you feel as though you need a refresher course in heart anatomy and physiology? If that's the case NOVA has put together an entertaining, informative interactive site. So why not take a moment and visit The Electric Heart.
Also of value for students and patients is The Heart Center Online. Here you can take quizzes, review the latest cardiac treatments, and learn a host of information about your heart and blood. Additionally, you might want to check out Heart1 for more information on tests, procedures, and the latest in heart research.
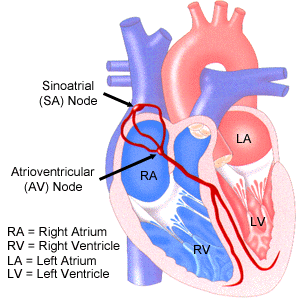
As the propagation of the electrical impulse travels down the wall of the right atrium it reaches the Atrioventricular Node or AV Node. This is another specialized area of the heart whose function is to conduct the electrical impulse downward into the ventricles through the Bundle branches and ultimately into the Purkinje System. To view an animation of this conduction process in easy-to-understand language, take a moment and click here.
Of course things don't always work the way they should, and rhythm disturbances sometimes do occur. For a better understanding of what can go wrong and why, you will want to read the prepared text on abnormal conduction.
The electrocardiogram is a very valuable diagnostic tool for determining conduction problems within the heart (as well as other cardiac pathology); and so that you may become familiar with what cardiac tracings look like, and how they are interpreted, I would like to refer you to a specialized library: The Library of Electrocardiography.
Our discussion of the heart will continue in the Lecture Hall.
If you have a specific question about the heart, or if you have a medical question of any kind, you can ask it by visiting my Consulting Room.
