|
GTABLE DATA PROCESSING
In addition to shape object, XBit provides gtable object
to handle shape object related attribute data. An XBit table
object is an encapsulation of code and data with both C and Tcl API.
A table object can receive data from either scripts or files. Currently,
a gtable object can read data from and write data to a table (.dbf)
file.
Create
A GTable Object. A gtable object is created using
Tcl command
gtable.create gtableObject ?options?
where gtableObject is a new Tcl command to
identify and interface to an instantiated table object via Tcl scripts.
Options for creating a table object include -file and -update.
Option -file specifies a table (.dbf) file to initialize the table
object. Option -update can be configured to either 0 or 1.
When a client opens a gtable object via its C API, it can add a
call back function for the updating event. When option -update
is set to 1, a gtable object will invoke call back functions of its clients
whenever its contents have been changed.
Define
A GTable Object. To define a newly
created table object, use the following command,
gtableObject define
fieldDefinition
?filedDefinition?...
where fieldDefinition
is a field definition list consisting of four elements {fieldName
type width decimal}, where fieldName
speicfies the name of the field and must be a string with no space, type
specifies the data type of the field and must be one of the following characters:
N
(for numerical data type), C (for character string),
L (for
logical data type), D (for date data type), M (for memo text),
width
is an integer to specify the size of the data element, decimal
is an integer to specify the number of decimals of a numerical data type
and must be 0 for data types C, L, D or M.
To add new data fields into a gtable object, use
the following command,
gtableObject addfields
fieldDefinitionList
?fieldList?
where fileDefinitionList
is a list of field definition, fieldList is
a list of initial values for the newly added fields. The added fields
are always appended at the end of the current field list.
To insert new data fields into a gtable object,
use the following command,
gtableObject insertfields
position
fieldDefinitionList ?fieldList?
where position specifies
the index of the current field list to insert the new fields.
To delete a field, use the following command,
gtableObject delete
fieldName
Edit
A GTable Object. To add records into a gtable object,
use the following command,
gtableObject addrecord ?record?
where record specifies a list of data items
of a record to be appended at the end of the gtable object.
To insert records into a gtable object, use the following command,
gtableObject insertrecords position
?nRecords? ?recordList?
where position specifies the position to insert
the records, nRecords specifies the number
of records to insert and recordList specifies
a list of records to intialize the newly inserted records. If nRecords
and recordList are not specified, one empty
record will be inserted. If recordList is not specified, nRecords
of empty records will be inserted.
To delete records, use the following command,
gtableObject deleterecords ?index?...
The deleted records are only marked as deleted and can be undeleted by
the following command,
gtableObject undeleterecords ?index?...
To erase deleted records permanently, use the following command,
gtableObject purge
To set a record's field value, use the following command,
gtableObject setfield recordIndex
fieldIndex value
To set a whole record, use the following command,
gtableObject setrecord index
record
To save a gtable object into a file, use the following command,
gtableObject save fileName
GTable
Data Analysis. For a gtable object analysis, the
first thing to do is to retrieve primative information of a gtable object
using the following command,
set info [gtableObject info]
The returned info is a list of field definitions.
Each field definition is a list of {name type length decimal},
where name is the field name, type is
the field data type, length is the size of
the field in bytes and decimal is the number
of decimals if the field is of type N (i.e., numerical type).
A tabular data anaylysis involves both data retrieval and comparison.
To retrieve a gtable record, use the following command,
set record [gtableObjectgetrecord
index]
The returned record is a list of field values
of the specified record.
To retrieve a field value of a gtable record, use the following command,
set filedvalue [gtableObject
getfield
recordIndex
fieldIndex]
Tcl procedures may be developed to process the retrieved data against interested
attribute values and selection can be performed based on the processing
result.
To select/unselect records, use the following commands,
gtableObject aselect ?index?...
gtableObject select ?index?...
gtableObject selectonly ?index?...
gtableObject unselect ?index?...
gtableObject unselectonly ?index?...
The aselect command reverses the selection
status of selected records to unselected and unselected records to selected.
The select command adds the selected records
into the already selected record pools. The selectonly
command selects the specified records and unselects others; the unselect
command adds the unselected records into the already unselected record
pool. The unselectonly command unselects
the specified records and selects others.
To combine data retrieval, process and selection together, use the following
command,
gtableObject match predicateScript
action
where predicateScript is a Tcl scriptic predicate
with field values of a record and action is
a build-in command and must be one of select, unselect, selectonly,
unselectonly,
aselect,
and list. A predicateScript returns
1 if its evaluation is true or 0 otherwise. The match
command evaluates every records of a gtable object with perdicateScript
and fires
action against the record if an evaluation
result of predicateScript is 1. A field
value may be specifed in a predicate script by its name following a "%".
For example, "expr %AREA < 500.0" is a predicate script expression that
returns 1 if the value of the field AREA is less than 500. A record may
be specified by %{RECORD} and a record index %{INDEX}. A select
action selects the record if evaluation of predicateScript
is true. An unselect action unselects the record if evaluation
of predicateScript is true. An aselect
action reverse the selected records to unselected and vise verser if evaluation
of predicateScript is true. A selectonly
action selects the record if evaluation of predicateScript
is true and unselect it otherwise. An unselectonly action
unselects the record if evaluation of predicateScript
is true and selets it otherwise. A list action adds the index
of a record into a return list if evaluation of predicateScript
is true.
Using
GTable Object in Map Processing. A gtable object
may be used with a shape object for map display with a gcanvas widget.
A gtable object created from a shape .dbf file provides additional attributes
for the shape object. A user may use these attributes for additional
text annotations and graphic labels in map display. In addition,
a user may select records with predicate scripts and use the result to
directly match the shape object in display. In the following example,
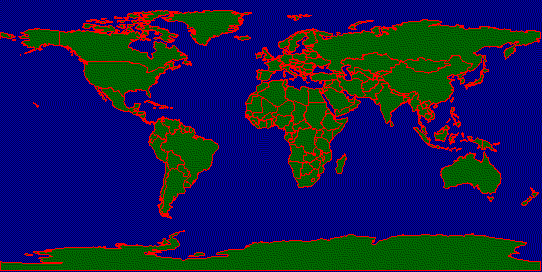
we first create a world map with a shape data set.
# create a shape object and its associate gtable
object
shape.create countries -file cntry94.shp
gtable.create countries.tb -file cntry94.dbf
# create a gcanvas widget and display the shape object
gcanvas .map -mx 1.5 -my -1.5 -viewx -180 -viewy 90 -highlightthickness
0 -update 1 -bg darkblue
.map create object 0 0 -object countries -outline red
-fill darkgreen
pack .map -expand 1 -fill both
Then we highlight regions with areas greater than 1000000 square miles
and draw proper text labels:
# In the gtable object, find indices of the regions
with areas greater than 1000000 square miles
set selectedIndices [countries.tb match "expr %AREA >
1000000" list]
# match the shape object selection with its associated
gtable selection
countries match countries.tb
# clone a shape object of the selected shape records
countries clone bigregions selected
# reselect the original shape object and display the cloned
shape object
countries select
.map create object 0 0 -object bigregions -outline green
-fill brown
# find the field index of the NAME field
set fieldIndex 0
foreach {name type length decimal} [countries.tb info]
{
if {$name == "NAME"} break
incr fieldIndex
}
# annotate the areas with proper text label
foreach index $selectedIndices {
set name [countries.tb getfield
$index $fieldIndex]
set centroid [lindex [countries centroid
$index average] 0]
set x [lindex $centroid 0]
set y [lindex $centroid 1]
.map create text $x $y -text $name
-anchor center -fill yellow
}

[HOME][CONTENTS][DOWNLOAD]
|
|