

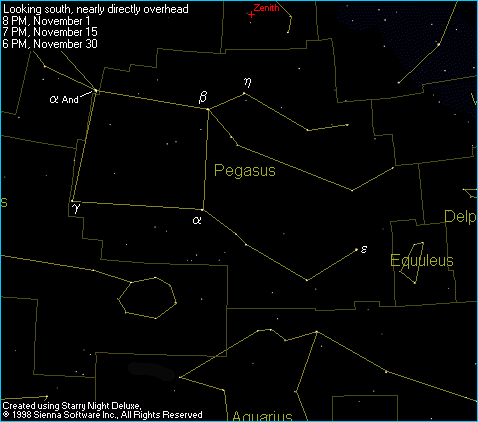
This is another star chart of Pegasus to help you recognize the constellation in the sky, but this time I added some Greek letters next to some of the brightest stars so that we can attach some names to what you're seeing in the sky. I always find that my appreciation for the sky is enhanced when I know a little bit about the things I'm viewing. As you may know, many but not all of the brightest stars in the sky have proper names (ie: Betelgeuse in Orion). Another method of naming stars involves the use of Greek letters and the genitive case of the Latin name, known as the "Bayer name". For example, the Bayer name for Markab would be Alpha Pegasi (pronounced PEG-ah-sigh). Anyway, this is a list of some of the major stars in Pegasus with a brief description of each. Just match the star on the list to the greek letter in the picture!
Markab [ Alpha (a) Pegasi]: The brightest star in Pegasus, Markab shines at magnitude +2.5 from the bottom right corner of the Great Square of Pegasus at the times given on the chart at right. The name comes from an Arabic word which means saddle, or generally anything ridden upon. Another Arabic name for the star is Matn al Faras, the Horse's Shoulder, which more accurately describes the position of the star as shown on classical drawings. Markab lies about 101 light-years away and is about 100 times more luminous than our own Sun.
Scheat [Beta (b) Pegasi]: Forming the top right corner of the Great Square at the times given on the chart, this star represents the point where the front legs of Pegasus join his body. Indeed, the star's name means "the Upper Part of the Arm". Scheat is actually a pulsating variable star, shining between magnitude +2.3 and +2.7 over an unpredictable period. Such a small change in magnitude will be a challenge to detect visually, especially without a regular interval to go by. Scheat lies about 176 light-years away.
Algenib [Gamma (g) Pegasi]: The name Algenib comes from either the Arabic phrase Al Janb, which means "the Side", or Al Janah, which means "the Wing", and the star forms the bottom left corner of the Great Square. Shining at magnitude +2.8 despite its distance of 490 light-years, Algenib has an amazing luminosity about 1900 times that of our own Sun.
Enif [Epsilon (e) Pegasi]: Enif represents the nose of Pegasus as drawn on most classical star maps, and the Arabic phrase from which the name is derived has the same meaning. You can best find Enif by first locating g and a forming the southern edge of the Great Square. Enif lies about 20º further along a straight line drawn from g to a. Enif shines at magnitude +2.4 with and lies about 520 light-years away.
Matar [Eta (n) Pegasi]: Matar is located about 175 light-years away and shines in our sky at magnitude +2.9. This star is the brightest among those that make up the forelegs of Pegasus.
Alpheratz [Alpha (a) Andromedae]: Shining at magnitude +2.1, Alpheratz is the brightest star in the Great Square asterism, but unfortunately it no longer belongs to Pegasus. Prior to this century, Alpheratz was actually "shared" by Pegasus and Andromeda, and on some old star maps the star is designated as Delta (d) Pegasi. In 1930, the International Astronomical Union officially set the boundaries to the constellations, and Andromeda gained sole possession of Alpheratz.
