|
| LinkExchange Member | Free Home Pages at GeoCities |
|
|
| LinkExchange Member | Free Home Pages at GeoCities |
|
|


|
Tropical Rain Forest Layers 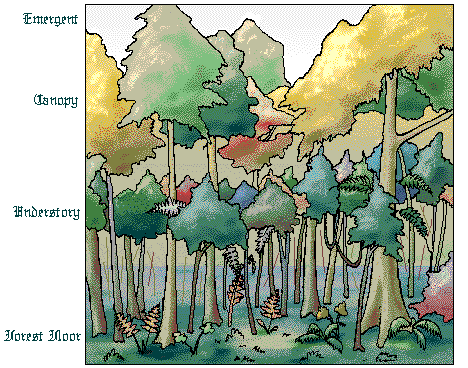
Tropical rain forests have four layers.
If your following FrostFlowers RainForest Trek click HEREEmergent Layer These giant trees thrust above the dense canopy layer and have huge mushroom-shaped crowns. These trees enjoy the greatest amount of sunlight but also must endure high temperatures, low humidity and strong winds.
Canopy Layer
The broad, irregular crowns of these trees form a tight, continuous
If your following FrostFlowers RainForest Trek click HERE
Understory
Receiving only 2-15% of the sunlight that falls on the canopy, the understory is a dark place. Forest Floor The forest floor receives less than 2% of the sunlight and consequently, little grows here except plants adapted to very low light. On the floor is a thin layer of fallen leaves, seeds, fruits and branches that very quickly decomposes. Only a thin layer of decaying organic matter is found, unlike temperate forests.
 Soil Most tropical forest soils are very poor and infertile. Millions of years of weathering and torrential rains have washed most of the nutrients out of the soil. More recent volcanic soils, however, can be very fertile. Tropical rain forest soils contain less organic matter than temperate forests and most of the available nutrients are found in the living plant and animal material.
Nutrient Recycling
Constant warmth and moisture promote rapid decay of organic matter. When a tree dies
|

|
What makes Tropical Rain Forests Special?
|
|
Comparison of Where Nutrients are Found in an Ecosystem
Comparison of Where Nutrients are Found in an Ecosystem
Based on the averaging of major nutrients.
|
| Tropical Rain Forest | Oak Woodland |
|---|---|
| 52% in Vegetation | 31% in Vegetation |
| 48% in Soil | 69% in Soil |








|



|