|
Online Dictionary
All these definitions are also at individual links - ATP,
Photosynthesis, Cellular Respiration
(This is for easy access)
Listed Alphabetically
ADP | Aerobic Processes | Anaerobic
Processes | Alcoholic Fermentation | ATP | Autotrophs
| Biology | Calvin Cycle | Carbon
Dioxide fixation | Carotenoids | Chloroplasts
| Chlorophyll | Cell | Cell
Membrane | Cellular Respiration | Concentration Gradient | Cytoplasm
| FAD | FADH2 | Glycolysis
| Electron Transport Chain | Enzyme
| Fermentation | Heterotrophs |
Krebs Cycle | Lactic Acid
Fermentation | Metabolism
| Mitochondria | Molecule
| NAD+ | NADH
| NADPH
| Nucleic Acids | Nucleotide
| Organelle | Photosynthesis
| Pigment | Proteins | Pyruvate
| Thylakoids
ADP = organic molecule; adenosine diphosphate;
has two phosphate groups, a base, and sugar
Aerobic Processes = processes that use metabolism with air
Alcoholic Fermentation = Fermentation that produces
Ethanol
Anaerobic Processes = processes that uses metabolism
without air
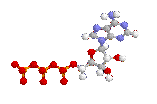
ATP = organic molecule that functions as the main energy
source of cells; adenosine triphosphate; has three phosphate groups, a base
(adenine) and a sugar (ribose)
Autotrophs = plants and certain bacteria that undergo
photosynthesis
Biology = study of life
Calvin Cycle = one of the many methods of carbon
dioxide fixation, used to produce a three-carbon sugar with the help of enzymes
Carbon Dioxide fixation = transfer of
carbon dioxide to organic compounds
Carotenoids = pigments that produces the fall leaf
colors, and colors of fruits, vegetables, and flowers
Chloroplasts = organelles that use light energy to
make carbohydrates from carbon dioxide and water
Chlorophyll = primary pigment involved in
photosynthesis
Cell = smallest component that can operate all of the
processes of life
Cell membrane = part of a cell that surrounds and
encloses the cytoplasm
Cellular Respiration = process where
heterotrophs harvest the energy in food molecules
Concentration Gradient = difference in the
concentration of a substance
Cytoplasm = the interior of a cell
Electron Transport Chain = series of
molecules where excited electrons move through
Enzyme = protein that speeds up chemical reaction
FAD = electron acceptor
FADH2 = electron carrier
Fermentation = recycling of NAD+ to
continue anaerobic glycolysis
Glycolysis = process that breaks down a
molecule of glucose to two three-carbon pyruvates
Heterotrophs = humans and other animals that get
their energy by undergoing cellular respiration
Krebs Cycle = series of enzyme-assisted
reactions
Lactic Acid Fermentation = Fermentation
that produces Lactate
Metabolism = the sum of all the chemical reactions
carried out in a chemical equation
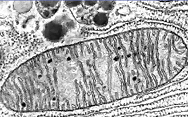
Mitochondria = organelle that makes ATP
Molecule = group of atoms held together by covalent bonds
NAD+ = electron acceptor
NADH = electron carrier
NADPH = electron carrier in photosynthesis that provides
"excited" electrons
Nucleic acids = long chain of nucelotides
Nucleotide = part of a nucleic acid that consist of a
nitrogen base, a sugar, and a phosphate group
Organelle = structure in a eukaryote cell that has a
specialized function
Photosynthesis = process where living organisms use
energy from sunlight to make organic compounds converting light energy to
chemical energy
Pigment = light-absorbing substances
Proteins = chain of amino acids
Pyruvate = Ion (molecule that has lost or gained one or
more electrons) of a three-carbon organic acid called pyruvic acid
Thylakoids = internal membranes of chloroplasts
|