|
For information on any picture rest the mouse
arrow (pointer) over it.
SCROLL
DOWN FOR MORE PICTURES
















Corbis/AFP
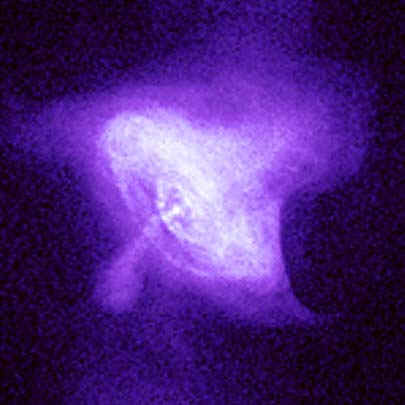
The Crab Nebula at X-ray wavelengths
A brilliant ring surrounds a neutron star at
the heart of the Crab Nebula, the remnant of a
supernova explosion that was seen from Earth
in 1054 AD. This image of the Crab Nebula at
X-ray wavelengths was taken by the Chandra
X-ray Observatory.

REUTERS/HO
Chandra X-Ray Observatory
This artist's impression depicts the Chandra
X-Ray Observatory. The orbiting observatory
has detected many new astronomical X-ray
sources and produced a wealth of
high-resolution images of stars, nebulas,
and galaxies.

STS-110 Shuttle Crew, NASA
International Space Station
A cooperative effort of 16 nations, the
International Space Station (ISS) is the
largest space station ever constructed. It
serves as an orbiting research platform. This
photograph was taken from the space shuttle
Atlantis.

Material created with support to AURA/ST Sci
from NASA contract NAS5-26555 is reproduced
here with permission/Courtesy of E. Karkoschka
(University of Arizona), and NASA
Saturn’s Atmosphere
This infrared photo of the planet Saturn has
been color coded to indicate the cloud level
in Saturn’s atmosphere. Violet and blue
represent areas in which Saturn’s atmopshere
is clear down to the main cloud layer. Green
and yellow show layers of haze above the main
cloud layer (yellow represents thicker haze).
Red and orange indicate the highest level of
clouds, thicker than the haze. White areas are
areas of the atmosphere with high levels of
water vapor. The bright dots at the upper
right and lower left of the picture are
Saturn’s satellites
Tethys and Dione, respectively. The Hubble
Space Telescope took this image in 1998.

NASA
Planet and Satellite Sizes
Some of the largest moons in the solar system
are as large as or larger than the smallest
planets. Depicted here to scale are top
row, from left to right, Earth, Mars,
Mercury, and Earth's moon; second row,
Jupiter’s satellites
Io and Europa; third row, Jupiter’s
moons Ganymede and Callisto; and bottom
row, Venus and Saturn’s moon Titan.


REUTERS/Shamil Zhumatov
Space Tourist Dennis Tito
Dennis Tito, the world’s first paying space
tourist, raises his hands after landing in a
remote part of Kazakhstan on May 6, 2001. Tito
and two Russian cosmonauts returned to Earth
in the Soyuz space capsule following a trip to
the International Space Station. Tito, a
California businessman, hailed his journey in
space as a ”trip to paradise.”










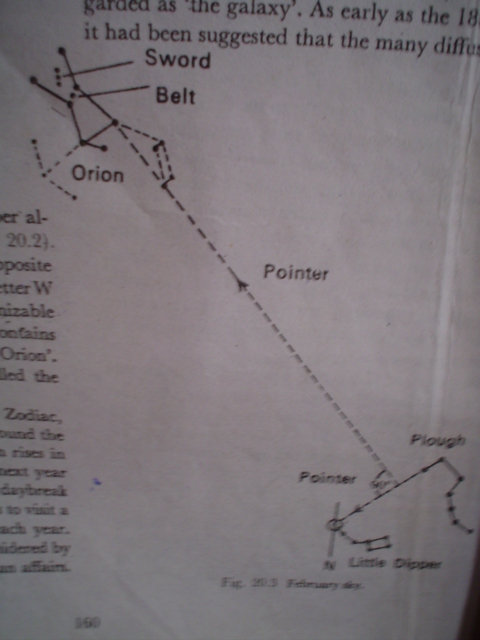
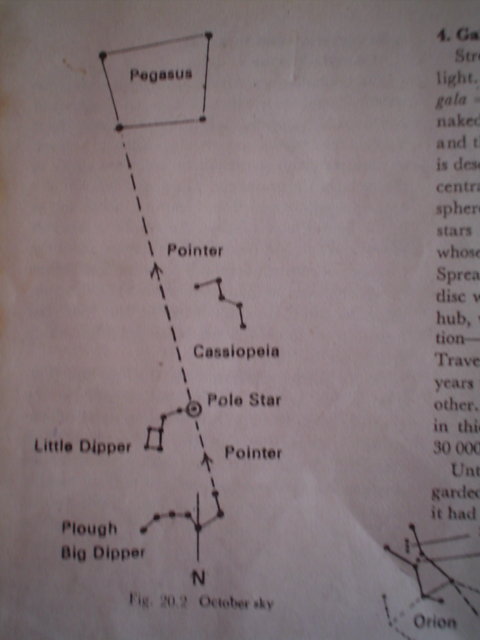

Orion Nebula
Located in the constellation Orion, 1,600
light-years away from Earth, the Orion Nebula
(M 42) is a bright cloud of gas and dust where
stars are in the process of being born. The
Orion Nebula looks bright because it reflects
light from the multiple star Theta Orionis,
located on one side. Radiation from new stars
in the Nebula lights up hydrogen in its outer
regions, causing the gas to glow with its
characteristic red color. M 42 is spread
across more than 15 light-years of space.

Orion Nebula in Infrared
This image of the Orion Nebula was taken in
infrared radiation—radiation with
wavelengths longer than visible light—and
given false visible colors. The Orion Nebula
is a cloud of gas and dust that surrounds new
stars. The young stars light up the nebula and
cause it to glow.

Photo Researchers, Inc./ESA/ISO, CEA Saclay
and ISOCAM Consortium
Stellar Nursery in Infrared
The Infrared Space Observatory (ISO) detected
infrared radiation in space. It could see
through clouds of interstellar dust because
infrared radiation is not blocked by the dust
as much as visible light is. The ISO took this
picture of new stars forming out of a cloud of
dust and gas. The stars are not visible to
optical telescopes because the visible light
that they emit is blocked by the dust
surrounding them.
PICTURE
CREDITS
The
pictures with captions are taken from Encarta
Reference Library
Other
sources include:
NASA,
JPL
ESO
|