Project Map
Back to First-Page to View Table of
Contents
|
[Source: Report of RBI Working Group on Credit Derivatives]
Credit Linked Deposits/ Credit Linked Certificates of Deposit
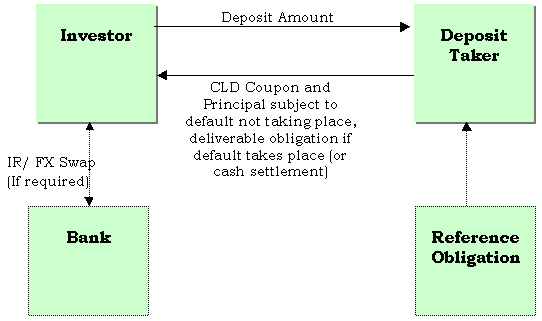
14. Credit Linked Deposits (CLDs) are structured deposits with embedded default swaps. Conceptually they can be thought of as deposits along with a default swap that the investor sells to the deposit taker. The default contingency can be based on a variety of underlying assets, including a specific corporate loan or security, a portfolio of loans or securities or sovereign debt instruments, or even a portfolio of contracts which give rise to credit exposure. If necessary, the structure can include an interest rate or foreign exchange swap to create cash flows required by investor.
15. In effect, the investor is selling protection on the reference obligation and earning a premium in the form of a yield spread over plain deposits (this is akin to the investor investing money or buying a bond issued by the Reference Entity to earn higher yield than plain deposits). If a credit event occurs during the tenure of the CLD, the deposit accelerates and the investor would get the Deliverable Obligation instead of the Deposit Amount.
Credit Linked Deposits / Certificate of Deposits.
16. "Credit Linked Deposits, Credit Linked Certificates of Deposits or Credit Linked Notes" are transactions under which deposit taker/note issuer is the Protection Buyer and the depositor/investor is the Protection Seller, such that:
On start date, Protection Seller deposits/pays notional amount to Protection Buyer; and On periodic interim dates, Protection Buyer pays to Protection Seller pre-agreed coupon on notional amount; and If a Credit Event does not occur, Protection Buyer redeems deposit/note at full notional amount at maturity; or If a Credit Event occurs and physical settlement applies, the deposit/note shall accelerate and Protection Buyer shall deliver the Deliverable Obligations to Protection Seller; or If a Credit Event occurs and if cash settlement applies, the transaction shall accelerate and Protection Seller shall pay to Protection Buyer the prevailing market value of the Deliverable Obligations upon occurrence of the Credit Event.
Characteristics
Notes can be structured as Medium Term Notes or trust certificates - (This shall be subject to regulatory guidelines, if any) Amount of principal redemption is linked to the recovery value of the Reference Obligations. In the event of default, principal redemption may be cash or physical delivery of the Reference Obligations In the case of no default, investors continue to have exposure to the Deposit taker/ issuer of the Medium Term Notes or the underlying collateral of the trust Deposits/ Notes can also be structured to provide varying principal protection
Uses and Benefits of CLDs
Access - CLDs enable investments in credits when there are no cash markets available for that credit. Synthetic Maturity - CLDs can be created with customized maturity structures and credit features that are otherwise not available in the cash market. Credit Lines - Banks can issue CLDs that are linked to loan credits in their portfolios. This can free up credit lines to a particular borrower, as well as give non-bank investors access to credit opportunities that may otherwise not normally be available in the capital markets. Elimination of Counterparty risk - As the CLD is a funded transaction by the investor in the CLD, there is no counterparty risk as there would be with buying protection using a credit default swap.
|


