Binomial
Formula
Factorial
For 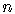 a natural number, the factorial is the product of the first
a natural number, the factorial is the product of the first
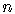 natural numbers.
natural numbers.
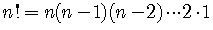
In particular,

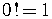 .
.
Notice that we can group factors and write
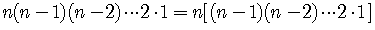 .
.
The product within the brackets is 
Therefore, we have the
Recursion Formula
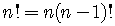
See example 1, page 826.
Combinatorial Symbol
For nonnegative integers 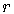 and
and 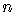 ,
,

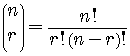

Other notations for the combinatorial symbol are
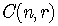 ,
,
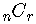 , or
, or
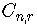 .
.
These symbols are also called binomial coefficients.
See Example 2, page 827.
Binomial Formula
For 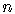 a positive
integer
a positive
integer
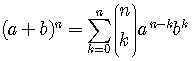 .
.
Observations
1)
The expansion of 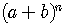 has
has 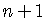 terms.
terms.
2)
As we move from the left of the expansion to the right of the expansion,
the powers of 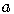 decrease and the powers of
decrease and the powers of 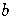 increase.
increase.
3)
In each term, the sum of the powers of 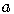 and
of
and
of 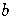 always
add up to
always
add up to 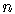 .
.
Example 1

The number of terms in the expansion is 5+1.
As the powers of a decrease from 5 to 1, the powers of b
increase from 1 to 5.
In each term, the sum of the powers of a and b always
add up to 5.
Example 2
Expand 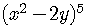 .
.
In the binomial formula let 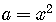 ,
,
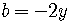 , and
, and
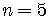 .
.


Evaluate the binomial coefficients and do the algebra.



See Examples 4, page 830.
Suppose we want to determine only a particular term in an expansion.
The 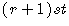 Term of the Binomial Expansion
Term of the Binomial Expansion 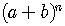 is
is
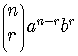 .
.
Example 3
Find the 5th term in the expansion of
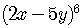 .
.
We must write the number 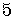 so it is
in the form,
so it is
in the form, 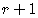 ,
,
given in the formula.
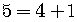 ,
so
,
so 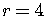 .
.
The other substitutions are
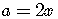 ,
,
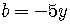 , and
, and
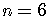 .
.
Then the 5th term in the expansion is

or
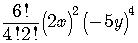 or
or 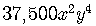 .
.
See Example 5, page 831.
top
next Multiplication
Principle, Permutations and Combinations
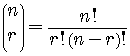

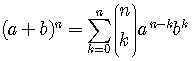 .
.

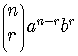 .
. 