-
A

- abacus an oriental (far east) counting device and calculator.
-
abelian or Hyperelliptic Function
is a generalisation of an elliptic function. It is a function of two variables with four
 periods. In a similar way to an elliptic function it can also
be regarded as the inverse function to certain integrals ( called
abelian or hyperelliptic integrals ) of this form where R is a
polynomial of degree greater than 4.
periods. In a similar way to an elliptic function it can also
be regarded as the inverse function to certain integrals ( called
abelian or hyperelliptic integrals ) of this form where R is a
polynomial of degree greater than 4.
-
abscissa the x-coordinate in a normal two-dimensional coordinate system.
The abscissa of the point (a, b) is 'a'.
-
absolute value The symbol for absolute value is usually a pair of vertical
lines containing the number. The symbolism |4| is read as "The absolute value
of four". The absolute value of a real number is its distance from zero,
so |4| = |-4| = 4 ... which is the distance of the number from zero. The
positive value.
-
abundant number is an integer for which the sum of its proper divisors is greater than the number itself.
i.e., the proper divisors of 12 are 1, 2, 3, 4, 6 which sum to 16. See also: perfect number deficient number
-
acceleration the rate of change, the derivative of velocity. If position
is represented by s(t), then velocity is s'(t) and the
acceleration is s"(t). The change in velocity divided by the change
in time. See Acceleration, compare units used.
-
acute angle a positive angle that measures less than 90 degrees ...
an angle in the range of 0 degrees to 90 degrees. See
complementary
-
acute triangle a triangle in which each of its angles measures less
than 90 degrees ... a triangle in which all the angles are acute.
-
additive identity The number zero is called the additive identity because
when you add it to a number, N, the result you get is the same number, N
... 0 + 5 = 5.
-
additive inverse the additive inverse of a number, N, is the number
that when you add it to N, the result that you get is zero. The
additive inverse of 7 is -7 ... 7 + -7 = 0.
-
adjacent angles two angles that share both a common side and vertex.
-
altitude the perpendicular distance measured from the base of a figure
to the highest point of the figure.
-
Amicable numbers are a pair of numbers a, b for which the sum of the proper divisors of a equals b and the sum of the proper divisors of b is equal to a.
-
amplitude half the difference between the largest and smallest function
value of a periodic function.
-
Analytic number theory is number theory studied using methods like infinite series, convergence, etc. taken from analysis and especially from Complex analysis. It contrasts with algebraic number theory.
-
angle the union of two rays which have a common endpoint (starting point).
-
antecedent the hypothesis of conditional statement. The
"if" part of an "if-then" statement.
-
antiderivative the antiderivative of a function, f(x), is a
function, F(x), whose derivative is f(x). Also called the indefinite
integral.
-
apogee is the point where a heavenly body is furthest away from the centre of its orbit.
The nearest point is called the perigee.
-
apothem the perpendicular distance from the center to a side of a regular
polygon.
-
apotome is one of Euclid's categories of irrational numbers. A number of the form
 ( ( A - A -  B) is called a apotome.
The corresponding number with a + sign is called a binomial B) is called a apotome.
The corresponding number with a + sign is called a binomial
-
area The general term for the measurement of the amount of surface space
that is occupied or covered by a two dimensional figure ... from Latin.
-
arc the set of points on a circle that lie in the interior of a central
angle.
-
arc length given by the following:

-
arccos If x = cos y, then y = arccos x. The inverse of the cosine
function.
-
arccsc If x = csc y, then y = arccsc x. The inverse of the cosecant
function.
-
arccot If x = cot y, then y = arccot x. The inverse of the
cotangent function.
-
arcsec If x = sec y, then y = arcsec x. The inverse of the
secant function.
-
arcsin If x = sin y, then y = arcsin x. The inverse of the
sine function.
-
arctan If x = tan y, then y = arctan x. The inverse of the
tangent function.
-
argument The independent variable in a function.
-
arithmetic mean The sum of a set of numbers divided by the number of
numbers. Also called the average.
-
arithmetic sequence a sequence of numbers of the form a, a + b, a +
2b, a + 3b, ... , a + (n - 1)b. There is a constant 'adder' between two terms;
there is a constant 'difference' between two terms. Ex: 4, 7, 10, 13,
16, 19, 22, 25, ...
-
arithmetic series the sum of an arithmetic sequence. Ex: Given the
arithmetic sequence 3, 5, 7, 9, 11 ... the arithmetic series would be 3 +
5 + 7 + 9 + 11.
-
Ascension
The rising of a star above the horizon
-
associative property of addition (a + b) + c = a + (b + c)
-
associative property of multiplication (a * b) * c = a * (b * c)
-
asymptote a straight line that is a close approximation to a curve as the
curve is drawn; in other words, a line that a curve or function gets close
to but never crosses. The two most common types of asymptotes are horizontal
and vertical.
-
average same as arithmetic mean.
-
axiom a statement that is assumed to be true without proof.
Postulate.
-
axis of symmetry a line that passes through a figure in such a way
or image of the part of the figure on the other side of the line.
that the part of the figure on one side of the line is a mirror reflection
- azimuth
The azimuth is the arc of the horizon between the meridian (the direction North) and a vertical circle passing through a heavenly body.
-
B
-
Bernoulli Numbers were defined by Jacob Bernoulli in connection with evaluating sums of the form can be generated using the formula:
 The sequence B0 , B1 , B2 ,...
x/(ex - 1) =
The sequence B0 , B1 , B2 ,...
x/(ex - 1) =  (Bnxn)/n!
though various different notations are used for them. The first few are: B0 = 1 , B1 = -1/2 , B2 = 1/6 , B4 = -1/30 , B6 = 1/42 , ...
They occur in many diverse areas of mathematics including the series expansions of tan(x). (Bnxn)/n!
though various different notations are used for them. The first few are: B0 = 1 , B1 = -1/2 , B2 = 1/6 , B4 = -1/30 , B6 = 1/42 , ...
They occur in many diverse areas of mathematics including the series expansions of tan(x).
-
beta function B (m, n) is defined to be the integral:
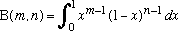 It can be defined in terms of the gamma function by:
It can be defined in terms of the gamma function by:
 Many integrals can be reduced to the evaluation of Beta functions.
Many integrals can be reduced to the evaluation of Beta functions.
- Bieberbach Conjecture is the conjecture which states that if f is a complex function given by the series
f (z) = a0 + a1z + a2z2 + a3z3 + ...
which maps the unit disc conformally in a one-one way then |an| n |a1| for each n.
It can be expressed as: The nth coefficient of a univalent function can be no more than n. n |a1| for each n.
It can be expressed as: The nth coefficient of a univalent function can be no more than n.
-
binary number system the number system that uses only 0's and
1's. The places in the binary numbers are: ...
2n ... 25=32, 24=16, 23=8, 22=4, 21=2, 20=1.
See Number Base
-
binomial an algebraic expression that is the sum of two terms (two monomials).
- binomial coefficients are the coefficients of powers of x in the expansion of (1 + x)n.
We have 
where the binomial coefficient  is the number of ways of choosing an (unordered) subset of size k from a set of size n. is the number of ways of choosing an (unordered) subset of size k from a set of size n.
The binomial coefficients are the entries in the Pascal triangle.
-
binomial theorem the theorem that tells shows the expansion of the general expression (a
+ b)n ... the binomial (a + b) raised to the nth power:
:
(x + y)n = xn + an-1xn-1y + an-2xn-2y2 + ... + yn
Where there is a descending power of the first term ... and an ascending power of the second term ...... with numeric values of Pascal's Triangle.
- biquadratic residue
A number m is a biquadratic residue modulon if m = r4 modulo n for some r.
-
bisect to cut or divide something in half.
- Boolean algebra is an algebra in which the binary operations are chosen to model the union and intersection operations in Set Theory. For any set A, the subsets of A form a Boolean algebra under the operations of union, intersection and complement.
- brachistochrone is a curve such that a particle descending along the curve under gravity will travel from one point to any other point in minimum time. The cycloid is such a curve, the stright line is the trial example.
-
C
-
cartesian coordinates a system whereby points on a plane are identified
by an ordered pair of numbers, representing the distances to two or three
perpendicular axes. The standard "x-y" coordinate system used in high school
algebra is a Cartesian Coordinate System ... with points in the plane having
cartesian coordinates (x, y).

- catenary
A catenary is the curve in which a heavy uniform chain hangs. Its equation is:
y = cosh(x) = 1/2 (ex + e-x) = 1 + x2/2 + x4/24 + .........
-
center the point that is the same distance from all the points on a
circle. The point that is the same distance from all the points on a sphere.
The point inside an ellipse where the major and the minor axes intersect.
The center of a circle that can be inscribed in a regular polygon.
-
central angle an angle that has its vertex at the center of a circle.
-
centroid the center of mass of an object. The point where the
object would balance if supported by a single support. The point in
a triangle where the three medians intersect.
-
chain rule dy/dx = dy/du * du/dx.
-
chord a line segment that connects two points on a curve.
-
circle the set of points in a plane that are a fixed distance from a given
point.
-
circular functions same as trigonometric functions.
-
circumcenter the point in a triangle that is the center of the circle
that can be circumscribed about the triangle. The intersection of the
perpendicular bisectors of the triangle.
-
circumference the distance around a closed curve. The circumference
of a circle is 2*pi*r where r is the radius of the circle.
- circumscribed
a circle is said to be circumscribed to a triangle or other polygon if the vertices of the polygon lie on the circle. The polygon
 is than said to be inscribed in the circle.
The (unique) circle circumscribed to a triangle is called the circumcircle and its centre is the circumcentre.
is than said to be inscribed in the circle.
The (unique) circle circumscribed to a triangle is called the circumcircle and its centre is the circumcentre.
-
circumscribed circle a circle that passes through all of the vertices of
a regular polygon.
-
closed interval an interval that contains its endpoints.
-
coefficient a constant that multiplies a variable. In Ax + By
= C, A and B are coefficients of x and y.
-
cofunction the cofunction of a trigonometric function, f(x), is equal
to f(pi/2 - x). The cofunction of the sine is the cosine. The cofunction
of the secant is the cosecant. The cofunction of the tangent is the cotangent.
-
collinear points are collinear if they lie on the same line.
-
commutative property a + b = b + a. a*b = b*a.
-
complementary angles two angles are complementary if their sum is 90
degrees.See acute.
-
completing the square the method of adding an expression to both sides
of an equation so that one side becomes a perfect square trinomial.
-
complex fraction a fraction that contains a fraction in its numerator
and/or denominator.
-
complex number the sum of an imaginary number and a real number written
in the form a + bi or r(cos x + isin x).
-
component the components in the vector (a, b, c) are a, b, and c.
-
composite function a function that consists of two functions arranged
in such a way that the output of one function becomes the input of the other
function.
-
composite number a natural number that is not prime.
-
concave a figure is concave if a line segment can be drawn so that
it goes in, out, then back into the figure.
-
conclusion the part of an if - then statement that follows the word
"then". Consequent.
-
conditional statement an 'if - then' statement.
-
cone the union of all line segments that connect a point and
a closed curve in a different plane from the point.
-
congruent shapes or angles are congruent if you could put one on top
of the other, and they would look like just one shape. Equal.
-
conic section parabola, hyperbola, ellipse, circle. Formed by
the intersection of a plane with a right circular cone.
-
conjecture a statement that seems to be true, but has not yet been
proven.
-
conjugate the conjugate of a complex number is formed by reversing the sign
on the imaginary part of the number. The conjugate of a + bi is a - bi.
-
conjunction a statement that is really two statements joined by the
word AND. Both parts must be true for the statement to be considered
true. (Concept of set intersection.)
-
consequent the part of an "if - then" statement that follows the "then".
Conclusion.
-
constant a value that does not change.
-
continuous a function is continuous if you can draw it without lifting
your pencil off the paper. y = f(x) is continuous at a if: 1. f(a)
exists. 2. lim as x-->a f(x) exists. And 3. lim as
x-->a of f(x) = f(a).
-
contrapositive the contrapositive of A-->B is Not B---->Not A.
-
convergent series an infinite series that has a finite sum is called
convergent.
-
converse the statement made by interchanging the hypothesis and the
conclusion of a statement.
-
convex a set of points such that for any two points in the set, the line
segment that connects them is also in the set.
-
coordinates a set of numbers that identifies the location of a point.
-
coplanar points that lie within the same plane are called coplanar.
-
corollary a statement that can be easily proven once a theorem is
proved.
-
cosecant csc x = 1/sin x
-
cosine In a triangle, the cosine of an angle = (length of the adjacent
side)/(hypotenuse)
-
cotangent cot x = 1/tan x
-
coterminal angles angles whose measures are 2kpi apart.
-
counting numbers natural numbers. The numbers you use to count.
-
critical point the point on a curve where the first derivative equals
zero. Extremum.
-
cube a solid figure with six square faces.
-
cubic a polynomial of degree 3.
-
cylinder the union of all line segments that connect corresponding
points on congruent circles in parallel planes.
-
D
-
decagon a polygon with ten sides.
-
decimal numbers the numbers in the base 10 number system.
-
decreasing function a function is considered to be decreasing if f(b)
< f(a) when b > a.
- Declination
the angular distance to a point on a celestial object, measured north or south from the celestial equator.
-
deduction a conclusion arrived at by reasoning.
- deficient number is an integer for which the sum of its proper divisors is less than than the number itself.
i.e., the proper divisors of 8 are 1, 2, 4, which sum to 7. See also
perfect number, abundant number.
-
definite integral the definite integral of f(x) between a and b represents
the area under the curve y = f(x) , above the x - axis, to the right of the
line x = a, and to
the left of the line x = b. The definite integral of f(x) = F(b)
- F(a) where F is an antiderivative function for f(x).
-
degree 1/360 of a full rotation. There are 360 degrees in a
circle. Unit of measure of an angle.
-
denominator the bottom part of a fraction.
-
dependent variable the output or matched value of a function.
-
derivative the rate of change (speed, slope, velocity) of a
function. The derivative at x of f(x) is the slope of the tangent line
at (x, f(x)). y' = f '(x) =the limit as delta approaches zero of [f(x
+ delta x) - f(x)] / delta x.
-
determinant the determinant | a b | ad -bc | c d |
-
diagonal the line segment connecting two nonadjacent vertices in a
polygon.
-
diameter the line segment joining two points on a circle and passing
through the center.
-
difference the result of subtracting two numbers.
-
differentiable a function is differentiable over an interval if it
is continuous over the interval and if the derivative exists everywhere
on the interval.
-
differential an infinitesimally small change in a variable, represented
by d, as in dx, or dy.
-
differentiation the process of finding a derivative.
-
digit the ten symbols, 0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, and 9 are
digits. Example: the number 365 has three digits: 3, 6, and 5.
-
dimension The dimension of a space is the number of coordinates needed
to identify a location in that space.
-
directly proportional y is directly proportional to x if y = kx.
-
discriminant the discriminant of a quadratic equation, ax2 + bx + c
= 0 is b2 - 4ac. The discriminant tells how many roots there are for the
equation and the nature of the roots.
-
disjoint having no elements in common.
-
disjunction an OR statement. (concept of set union.)
-
distributive property a(b + c) = ab + ac
-
divergent series a series whose sum is infinite.
-
dividend In a / b = c, a is the dividend.
-
division the opposite operation of multiplication.
-
divisor In a / b = c, b is the divisor.
-
dodecahedron a polyhedron with twelve faces.
-
domain the set of all possible values of the argument of a function.
-
E
-
e
2.718281828..... The base of the natural logarithm
function. e can be found from the infinite series:

of course taken to infinity.
-
eccentricity A number that indicates the shape of
a conic section. The eccentricity of an ellipse is given by
e = sqrt(a2 - b2) / a
-
element a member of a set.
-
ellipse the set of all points in a plane such that the sum of
the distances to two fixed points is a constant. The equation of an
ellipse with center at the origin is:
x2 + y2 = 1
-
ellipsoid a solid of revolution formed by rotating an ellipse
about one of its axes.
-
empty set a set that contains no elements.
-
equation a mathematical statement that says that two
expressions have the same value.
-
equilateral triangle a triangle that has three equal sides.
-
equivalent equations two equations whose solutions are the same.
For example: x + 3y = 10, and 2x + 6y
= 20.
-
even function a function that satisfies the property that f(x)
= f(-x).
-
even number a natural number that is divisible by 2.
-
event in probability, a set of outcomes.
-
evolute
The evolute of a curve is the envelope of the normals to the curve. This can also be thought of as the locus of the centres of curvature.
-
exponent a number that indicates the operation of repeated
multiplication.
-
exponential function a function of the form f(x) = ax, where
a is a constant known as the base.
-
extremum a point where a function reaches a maximum or a minimum.
-
F
-
factor one of two or more expressions that are multiplied together.
-
factor theorem If P(x) is a polynomial, then if P(r) = 0, then
(x - r) is a factor of P(x).
-
factorial
factorial of an integer n is the product 1.2.3. ... .n
It is denoted by n!
Generalised to non-integers, it is the Gamma function.
-
Fibonacci Sequence 1, 1, 2, 3, 5, 8, 13, 21, 34, 55, 89, 144,
233, 377.... The sequence in which every number is the sum of
the two preceding numbers. See Fibonacci.
-
field
is a ring in which non-zero elements have multiplicative inverses. Among the most important fields are the Real numbers R, the complex numbers C and various finite fields which are used in Number Theory and Combinatorics.
-
Fourier analysis
is the process by which one may write a periodic function on (say) the interval [0, 2
 ] as the sum of multiples of the functions sin(nx) and cos(nx). Where: f x) = a0 + a1cos(x) + b1sin(x) + a2cos(2x) + b2sin(2x) + ...
This is called the Fourier series of f and the numbers ai and bi are called the Fourier coefficients. ] as the sum of multiples of the functions sin(nx) and cos(nx). Where: f x) = a0 + a1cos(x) + b1sin(x) + a2cos(2x) + b2sin(2x) + ...
This is called the Fourier series of f and the numbers ai and bi are called the Fourier coefficients.
-
G
-
geometric mean the geometric mean of two numbers is the
square root of the product of the numbers. The geometric
mean of n numbers is the nth root of the product of the numbers.
-
geometric sequence a sequence of numbers of the
form a, ar, ar2, ar3,....., arn-1.
-
geometric series the sum of a geometric sequence.
-
Guldin's Theorem
If a plane figure is rotated about an axis in its plane then the volume of the solid body formed is equal to the product of the area with the distance travelled by the centre of gravity.
-
graph the graph of an equation is the set of points that
make the equation true.
-
great circle the circle formed by the intersection of a
plane passing through the center of a sphere.
-
greatest common factor the greatest common factor of two numbers,
a and b, is the largest number that divides both a and b evenly.
-
H
-
half plane the set of all points in a plane that lie on
one side of a line in the plane.
-
harmonic sequence a sequence is a harmonic sequence if
the reciprocals of the numbers in the sequence form an arithmetic sequence.
-
heptagon a polygon with seven sides.
-
Heron's formula a formula for the area of a triangle: A
= sqrt[(s(s - a)(s - b)(s - c))] where a, b, and c are the lengths of the
sides of the triangle, and s is half the perimeter.
 Area
Area
-
hexadecimal number a number written in base sixteen.
-
hexagon a polygon with six sides.
-
hexahedron a polyhedron with six faces. A regular
hexahedron is a cube.
-
hyperbola the set of all points in a plane such that the
difference of the distances to two fixed points is a
constant. The general equation for a hyperbola is:
-
hyperbolic functions the hyperbolic functions are defined
as follows:
-
-
hyperbolic cosine cosh x = (1/2)(ex
+ e-x)
-
-
hyperbolic sine sinh x =
(1/2)(ex - e-x)
-
-
hyperbolic tangent tanh x = sinh x/cosh x
-
hypotenuse the longest side of a right triangle. The
side opposite the right angle in a right triangle.
-
hypothesis a proposition that is being investigated, it has yet
to be proven.
-
I
-
i the basic unit for the imaginary number: i2 = -1.
-
icosohedron a polyhedron with 20 faces.
-
identity an equation that is true for all values of the variable.
-
identity element If * is an operator, then the identity
element, I, for * is the number such that I * a = a. The
identity for addition is zero, and the identity for multiplication is 1.
-
identity matrix a square matrix with ones along the
diagonal and zeros everywhere else. If I is an identity matrix, then IA =
A.
-
imaginary number a number of the form ni, where n is a
real number, and i2 = -1.
-
implication a conditional statement.
-
improper fraction a fraction with a numerator that is greater
than the denominator.
-
incenter the center of a circle that is inscribed in a triangle.
The intersection of the angle bisectors of the triangle.
-
incircle the circle that can be inscribed in a triangle.
-
increasing function a function is increasing if f(a) > f(b)
when a > b.
-
increment a small change, usually indicated by the greek letter
delta.
-
indefinite integral the sum of the antiderivative of a function
and an arbitrary constant.
-
independent variable the input number to a function.
-
infinity a limitless quantity.
-
inflection point a point on a curve such that the curve is concave
up on one side of the point, and concave down on the other side of the
point.
-
inscribed polygon a polygon placed inside a circle so that each
vertex of the polygon touches the circle.
-
integers the set of numbers containing zero, the natural numbers,
and all the negatives of the natural numbers.
-
integral If dF(x)/dx = f(x), then F(x) is an integral
of f(x). The area under the curve of a function above the x -
axis.
-
integrand a function that is to be integrated.
-
integration the process of finding an integral.
-
intercept the x-intercept of a curve is the point where the curve
crosses the x - axis, and the y - intercept of a curve is the point
where the curve crosses the y - axis.
-
inversely proportional y is inversely proportional to x if y
= k/x.
-
irrational number a number that cannot be expressed as the ratio
of two integers.
-
isometry a transformation of a figure that does not change the
distances of any two points in the figure.
-
isosceles triangle a triangle with at least two equal sides.
-
J
-
joint variation y varies jointly as x and z if y = kxz.
- K
- K informal abbreviation for thousand, used in expressions where the base unit is understood, such as "10K run" (10 kilometers) or "700K disk" (700 kilobytes or kibibytes). Note that "K" is also the symbol for the kelvin. Also note that the symbol for the metric prefix kilo- (1000) is actually k-, not K-.
- L
-
latus rectum the chord through the focus of a parabola parallel
to the directrix. The chord through a focus of an ellipse perpendicular to
the major axis.
-
Laplace transform
of a function f is defined by the integral:

-
law of cosines c2 = a2 + b2 - 2abCosC
-
law of sines a/sin A = b/sin B = c/sin C
-
least common denominator the least common denominator of
two fractions, a/b and c/d, is the smallest number that contains both b and
d as factors.
-
least common multiple the least common multiple of two
numbers, a and b, is the smallest number that contains both a and b
as factors.
-
lemma a theorem that is proved mainly as an aid in proving another
theorem.
-
like terms two terms each of whose parts, with the exception
of their coefficients, is the same.
-
line a straight set of points that extends off into infinity
in both directions.
-
line segment two points on a line, and all the points between
those two points.
-
logarithm if y = bx, then logb y = x.
-
logic the study of sound reasoning.
-
M
-
magnitude the magnitude of a vector is its length.
-
major arc an arc of measure greater than 180 degrees.
-
major axis the line segment connecting the two vertices
that are farthest apart in an ellipse.
-
matrix a table of numbers arranged in rows and columns.
-
maxima the points on a curve where the value is greater than
that of the surrounding points.
-
mean average, arithmetic mean.
-
median the number in a group of numbers such that there
are an equal number of numbers in the set greater than the number as are
less than the number.
-
midpoint a point, M, on a line segment, AB, such that AM = MC.
-
minima the points on a curve where the value is less than that
of the surrounding points.
-
minor arc an arc on a circle that is less than 180 degrees.
-
minor axis the shortest distance across an ellipse through the
center.
-
minute the unit of measure of an angle that is 1/60 of a degree.
-
mode the number that occurs most frequently in a set of data.
-
modulus the absolute value of a complex number.
-
monomial an algebraic expression that does not involve any additions
or subtractions.
-
multiplicand in the equation ab = c, a and b are multiplicands.
-
multiplication the operation of repeated addition.
-
multiplicative identity the number 1 is the multiplicative identity
because 1 * a = a for all a.
-
multiplicative inverse the number, b, that when multiplied by
a number, a, gives a result of 1. Reciprocal. b = 1/a.
-
N
-
natural logarithm the logarithm with the base of
e. Written: ln x.
-
natural numbers the counting numbers.
-
negative number a real number less than zero.
-
normal perpendicular.
-
null set same as empty set. A set with no elements.
-
number line a line on which every point represents a real number.
-
numeral a symbol that stands for a number.
-
numerator the top of a fraction.
-
O
-
obtuse angle an angle whose measure is greater than 90 degrees.
-
obtuse triangle a triangle with an obtuse angle.
-
octagon a polygon with 8 sides.
-
octahedron a polyhedron with 8 faces.
-
octal number a number in base 8.
-
odd function a function that satisfies the property that
f(-x) = -f(x).
-
odd number a whole number that is not divisible by 2.
-
open interval an interval that does not contain both its
endpoints.
-
ordered pair a set of two numbers in which the order
has an agreed upon meaning. Such as the cartesian coordinates (x, y), where
it is agreed that the first coordinate represents the horizontal position,
and the second coordinate represents the vertical position.
-
ordinate the second coordinate of a cartesian ordered pair.
-
origin the point (0, 0) on a Cartesian Coordinate System.
-
orthocenter the point in a triangle where the three altitudes
intersect.
-
orthogonal perpendicular.
-
P
-
parabola the set of all points in a plane that are equally distant
from a fixed point (called the focus) and a fixed line, (called the directrix).
-
paraboloid a surface that is formed by rotating a parabola about
its axis.
-
parallel two lines are parallel if they are in the same
plane and never intersect.
-
parallelepiped a solid figure with six faces such that
the planes containing two opposite faces are parallel. Each
face is a parallelogram.
-
parallelogram a quadrilateral with opposite sides parallel.
-
pentagon a five sided polygon.
-
percent a fraction in which the denominator is assumed
to be 100.
-
perfect number is an integer for which the sum of its proper divisors is equal to the number itself.
For example, 6 and 28 are both perfect numbers.
See also: abundant number, deficient number.
-
perimeter the sum of the lengths of the sides of a polygon.
-
period the measure of how often a function repeats its
same values.
-
periodic function a function that keeps repeating the same values.
-
permutation the permutation of n things taken j at a time
is: n! / (n-j)!
-
perpendicular two lines are perpendicular if the angle between
them is 90 degees.
-
pi the ratio of the circumference of a circle to its diameter.  See pi, this page explaining the magical relation of this number. See pi, this page explaining the magical relation of this number.
-
phi the ratio of the succesive numbers of the fibonacci series. 1.61803398501736 See phi, this page explaining the magical relation of this number.
-
plane a flat surfaces that stretches off into infinity.
-
polar coordinates a coordinate system of ordered pairs
in which the first number of the pair represents distance from the origin,
and the second number of the pair represents the angle of inclination from
the horizontal axis.
-
polygon the union of several line segments that are joined
together so as to completely enclose an area.
-
polyhedron a solid that is bounded by plane polygons.
-
polynomial an algebraic expression of the form:Example: axn + bx(n-1)
+ .......+ cx3 + dx2 + ex + k
-
positive number a real number greater than zero.
-
postulate a fundamental statement that is assumed to be
true without proof.
-
power a number that indicates the operation of repeated
multiplication.
-
prime number a number whose only factors are itself and
1.
-
product the result of two numbers being multiplied.
-
proper fraction a fraction whose numerator is less than
its denominator.
-
proportion: an equation of fractions in the form a/b =
c/d
-
proportional If y = kx, then y is said to be proportional
to x.
-
protractor a device for measuring angles.
-
pyramid the union of all line segments that connect a given
point and the points that lie on a given polygon.
-
Pythagorean Theorem the theorem that relates the three
sides of a right triangle: a2 + b2 = c2
-
pythagorean triple three natural numbers that satisfy the
pythagorean theorem.
-
Q
-
quadrant one of the quarters of the plane of the Cartesian
coordinate system
-
quadratic equation an equation involving the second power,
but no higher power of an unknown. The general form of a
quadratic equation in two unknowns is: Ax2 + Bxy + Cy2 + Dx + Ey + F = 0.
-
quadratic formula the formula that says that the solution
to a 2nd degree (quadratic) equation is as follows:

-
quadrilateral a polygon with 4 sides.
-
quartic a polynomial of degree 4.
-
quintic a polynomial of degree 5.
-
quotient the answer to a division problem.
-
R
-
R abbreviation for the real numbers.
-
radian the ratio of an arc of a circle to the radius of
the circle. On a unit circle, a full rotation around the circle
is 2pi radians. On any circle, a full rotation is 2pi r radians.
-
radius the distance from the center to a point on a
circle. The line segment from the center to a point on a
circle.
-
range the set of all possible values for the output of
a function.
-
ratio the ratio of two real numbers, a and b, is a/b.
-
rational number a number that can be expressed as the ratio of
two integers.
-
real numbers the union of the set of rational numbers and
irrational numbers.
-
reciprocal the reciprocal of a number, a, is 1/a, (a cannot
be zero).
-
rectangle a quadrilateral with four 90 degree angles.
-
rectangular coordinates same as Cartesian Coordinates.
-
reflection mirror image.
-
reflexive property x = x for all x. Every number
equals itself.
-
regular polygon a polygon in which all the angles are equal and
all of the sides are equal.
-
regular polyhedron a polyhedron whose faces are congruent,
regular polygons.
-
relation a set of ordered pairs.
-
remainder if m = nq + r, then m/q has quotient q and remainder
r.
-
repeating decimal a decimal in which the digits endlessly repeat
a pattern.
-
rhombus a quadrilateral with four equal sides.
-
right angle an angle whose measure is 90 degrees.
-
right circular cone a cone whose base is a circle located so
that the line connecting the vertex to the center of the circle is perpendicular
to the plane containing the circle.
-
right circular cylinder a cylinder whose bases are circles and
whose axis is perpendicular to its bases.
-
right triangle a triangle that contains a right angle.
-
root the root of an equation is the same as the solution to the
equation.
-
S
- saros a unit of time used in astronomy, mostly in predicting solar and lunar eclipses. The saros is equal to 6585.32 days (6585 days 7 hours 23 minutes), which is exactly 223 lunar months. (This is either 10 or 11 days more than 18 years, depending on the number of leap years during the period.) Astronomers in ancient times discovered that the saros is very nearly equal to 19 eclipse years (6585.78 days). This means that one saros after an eclipse the Sun, Moon, and Earth return almost exactly to the same position and another, very similar eclipse occurs. However, because of the 7 hours 23 minutes included, the Earth has turned about one third of a revolution and the new eclipse occurs about 116° of longitude west of the preceding one. After 3 saros, the eclipse returns nearly to its original location. Thus eclipses at a particular location tend to repeat with a period of 3 saros or 54 years 1 month. Thus the last total solar eclipse in North Carolina, on March 7, 1970, will repeat on April 8, 2024 and again on May 11, 2078. See saros
-
scalar a quantity that has size but no direction.
-
scalene triangle a triangle with three unequal sides.
-
secant a line that intersects a circle or a curve in two places.
-
secant the reciprocal of the cosine.
-
second the unit of measure of an angle that is 1/60 of a minute.
-
sector a region bounded by two radii of a circle and the arc
whose endpoints lie on those radii.
-
segment the union of a point, A, and a point, B, and all the
points between them.
-
series the sum of a sequence.
-
set a well defined group of objects.
-
similar two polygons are similar if their corresponding sides
are proportional.
-
simulataneous equations a group of equations that are all true
at the same time.
-
sine in a right triangle, the length of a side opposite an angle
divided by the length of the hypotenuse of the triangle.
-
skew two lines that are not in the same plane.
-
slope the slope of a line is the change in the vertical
coordinates/the change in the horizontal coordinates of any two points on
the line.
-
solid a three dimensional object that completely encloses
a volume of space.
-
sphere the set of all points in space that are a fixed distance
from a given point.
-
square a quadrilateral with four equal sides and four 90
degree angles.
-
square root of a number, x, is the number that, when multiplied
by itself gives the number, x.
-
subset A set, B, is a subset of another set, A, if every
element in B is also an element of A.
-
sum the result of adding.
-
supplementary two angles are supplementary if their sum is 180
degrees.
-
symmetric two points are symmetric with respect to a third
point if the segments joining them to the third point are equal.
Two points are symmetric with respect to a line if the line is
the perpendicular bisector of the segment joining the points.
-
T
-
tangent a line that intersects a circle in one point.
-
tangent in a triangle, (the side
opposite an angle) / (the side adjacent the same angle).
-
term a part of a sum in an algebraic expression.
-
terminating decimal a fraction whose decimal representation contains
a finite number of digits.
-
tetrahedron a polyhedron with four faces.
-
theorem a statement that has been proven.
-
trajectory the path that a body makes as it moves through
space.
-
transitive property the property that states that if a
= b, and b = c, then a = c.
-
translation a shift of the axes of the Cartesian Coordinate
System.
-
transit
The passage of a celestial body across the observer's meridian.
The passage of a smaller celestial body or its shadow across the disk of a larger celestial body.
-
transversal a line that intersects two other lines.
-
trapezoid a quadrilateral that has exactly two sides parallel.
-
triangle a three sided polygon.
-
trinomial a polynomial with exactly three terms.
-
U
-
union the union of two sets, A and B, is the set of all elements
that are either in A, or in B, or in both A and B.
-
unit vector a vector of length 1. It is customary
to designate i as the unit vector in the x direction, j as the unit vector
in the y direction, and k is the unit vector in the z direction.
-
V
-
variable a symbol used to represent a value.
-
vector a quantity that has both magnitude and direction.
-
velocity the rate of change of position.
The first derivative of the position function.
-
vertex the point on an angle where the two sides intersect.
-
volume measurement of space.
-
W
-
whole numbers the set of numbers that includes zero and all of
the natural numbers.
-
X
-
x-axis the horizontal axis in a Cartesian Coordinate System.
-
x-intercept the value of x at the point where a curve crosses
the x-axis.
-
Y
-
y-axis the vertical axis in a Cartesian Coordinate System.
-
y-intercept the value of y at the point where a curve crosses
the y-axis.
-
Z
-
zero the additive identity. The number that
when you add it to a number, n, you will net n as a result.
|
 periods. In a similar way to an elliptic function it can also
be regarded as the inverse function to certain integrals ( called
abelian or hyperelliptic integrals ) of this form where R is a
polynomial of degree greater than 4.
periods. In a similar way to an elliptic function it can also
be regarded as the inverse function to certain integrals ( called
abelian or hyperelliptic integrals ) of this form where R is a
polynomial of degree greater than 4.
 (
( A -
A -  B) is called a apotome.
The corresponding number with a + sign is called a binomial
B) is called a apotome.
The corresponding number with a + sign is called a binomial

 The sequence B0 , B1 , B2 ,...
x/(ex - 1) =
The sequence B0 , B1 , B2 ,...
x/(ex - 1) =  (Bnxn)/n!
though various different notations are used for them. The first few are: B0 = 1 , B1 = -1/2 , B2 = 1/6 , B4 = -1/30 , B6 = 1/42 , ...
They occur in many diverse areas of mathematics including the series expansions of tan(x).
(Bnxn)/n!
though various different notations are used for them. The first few are: B0 = 1 , B1 = -1/2 , B2 = 1/6 , B4 = -1/30 , B6 = 1/42 , ...
They occur in many diverse areas of mathematics including the series expansions of tan(x).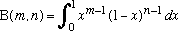

 n |a1| for each n.
It can be expressed as: The nth coefficient of a univalent function can be no more than n.
n |a1| for each n.
It can be expressed as: The nth coefficient of a univalent function can be no more than n.

 is the number of ways of choosing an (unordered) subset of size k from a set of size n.
is the number of ways of choosing an (unordered) subset of size k from a set of size n.
 is than said to be inscribed in the circle.
The (unique) circle circumscribed to a triangle is called the circumcircle and its centre is the circumcentre.
is than said to be inscribed in the circle.
The (unique) circle circumscribed to a triangle is called the circumcircle and its centre is the circumcentre.
 ] as the sum of multiples of the functions sin(nx) and cos(nx). Where: f x) = a0 + a1cos(x) + b1sin(x) + a2cos(2x) + b2sin(2x) + ...
This is called the Fourier series of f and the numbers ai and bi are called the Fourier coefficients.
] as the sum of multiples of the functions sin(nx) and cos(nx). Where: f x) = a0 + a1cos(x) + b1sin(x) + a2cos(2x) + b2sin(2x) + ...
This is called the Fourier series of f and the numbers ai and bi are called the Fourier coefficients.
 Area
Area



 See pi, this page explaining the magical relation of this number.
See pi, this page explaining the magical relation of this number.

