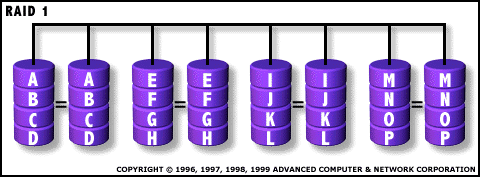
- One Write or two Read possible per mirrored pair
- Twice the Read transaction rate of single disks, same Write transaction rate as single disks
- 100% redundancy of data means no rebuild of data is necessary in case of disk failure, just a copy to the replacement disk
- Transfer rate per block is equal to single disks
- Simplest RAID storage subsystem design
|
- Highest ECC (Error Checking/Correction) disk overhead of all RAID types (100%) - inefficient
- Typically the RAID function is done by system software, loading the CPU/Server and possibly degrading throughput at high activity levels. Hardware implementation is strongly recommended
- May not support hot swap of failed disk when implemented in "software"
|