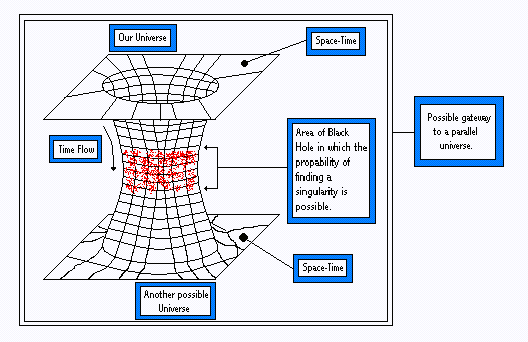
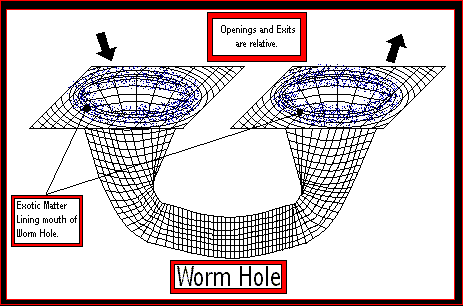
What is Time Dilation when talking about the Special Theory of Relativity ?  When objects move at non-relativistic speeds, space and time are
more constant and the speed of the object is relative, but when this
object moves at relativistic speeds, space and time are relative ,where
as; its speed is constant. This shows that time is not an absolute value
for the universe because it depends on your position and type of motion in
the universe. This speed reaches a limit at 3.0*10^8 m/s, which is the
speed of light. Objects that move at relativistic speeds under go time
dilation. This is one of the most important characteristics of objects
that move at relativistic speeds. The faster an object moves, the slower
its time is relative to an outside observer. This fact becomes very
powerful when an object moves at relativistic speeds. The formula
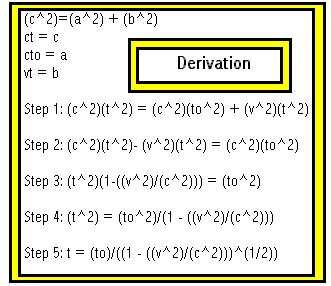
t = (to)/((1-((v^2)/(c^2)))^(1/2))
allows one to find the relativistic time. In this formula, (t) is the
relativistic time,(to) is the non-relativistic time, (v) is the speed
of the object, and (c) is the speed of light.
When objects move at non-relativistic speeds, space and time are
more constant and the speed of the object is relative, but when this
object moves at relativistic speeds, space and time are relative ,where
as; its speed is constant. This shows that time is not an absolute value
for the universe because it depends on your position and type of motion in
the universe. This speed reaches a limit at 3.0*10^8 m/s, which is the
speed of light. Objects that move at relativistic speeds under go time
dilation. This is one of the most important characteristics of objects
that move at relativistic speeds. The faster an object moves, the slower
its time is relative to an outside observer. This fact becomes very
powerful when an object moves at relativistic speeds. The formula
t = (to)/((1-((v^2)/(c^2)))^(1/2))
allows one to find the relativistic time. In this formula, (t) is the
relativistic time,(to) is the non-relativistic time, (v) is the speed
of the object, and (c) is the speed of light.
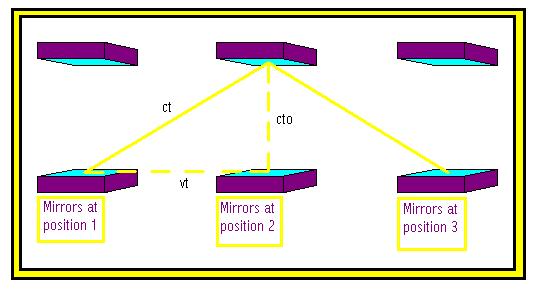


Back to
Neon's Virtual Office
This page hosted by 
 .Sheds a little
.Sheds a little 
 .Sheds a little
.Sheds a little