| Home │ IE Hijacking Part I │ IE Security Settings | ||
Clear the Internet Explorer cacheTopics in this article: [1] Internet Explorer cache revealed [2] How to delete the IE6 cache completely
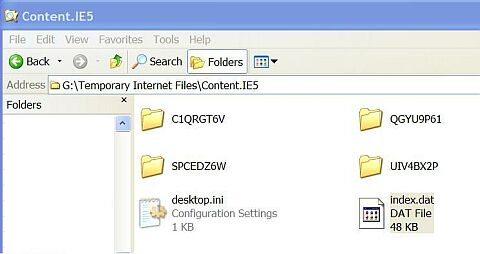
1. Internet Explorer Cache RevealedInternet Explorer stores (caches) the web pages you have read in a folder on your hard disc. The exact default location has changed with newer versions of Windows and you can change it and you can set IE to clear the cache on exit. In IE6, Tools, Internet Options, General window it is called Temporary Internet Files. In Windows XP with IE6, the default folder is in Documents and Settings\My Documents\Local Settings\Temporary Internet Files\Content.IE5\. Inside Content.IE5 there are at least four folders with different alpha-numeral names, an Index.dat file and a desktop.ini file. In this example the Content.IE5 folder location has been changed to another partition but the principle is the same.
Fig. 1. Inside the Content.IE5 folder
The folder can fill up with many other subfolders if you don't clean up regularly as in this case: it has 20 subfolders and the index.dat file has grown to 8.7MB (Fig. 2).
Fig. 2. Another Content.IE5 folder with 20 subfolders
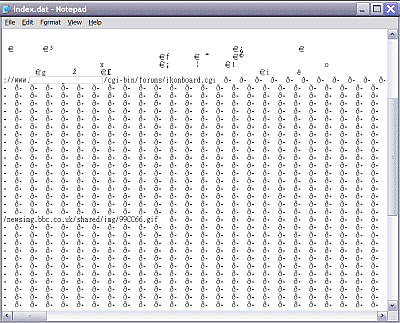
You cannot normally view these files in their normal location. The Local Settings folder is hidden by default; even if you unhide it you still cannot see any Content.IE5 folder or its subfolders in Windows Explorer. This folder would be made visible if you move your temporary internet files elsewhere. Where your temporary internet files are located (as in the above example) there will be another Content.IE5 folder with the same mysterious properties. Inside the Temporary Internet Files folder you will only see many files, shortcuts or individual elements of the web pages that you have read using IE (e.g. htm, jpg, jif, css, ram and txt) as if there are no subfolders. When you click the Delete Files button to delete your Temporary Internet Files in IE you do not really wipe everything although you will see a blank Temporary Internet Files Folder when you open it afterwards. (The files are still visible if your have Outlook Express open.) There is residual information left behind in the index.dat and the four subfolders, depending on your cache size. The index.dat file can grow in size with time and apart from causing occasional performance slowdown (see the KB article below) it is also a privacy issue for some people. If you open index.dat with Notepad you'll find the data (Fig. 3).
Fig. 3. Contents of the index.dat file
In DOS or the Windows command prompt the Temporary Internet Files directory, the Content.IE5 and each of its four subfolders have a system attribute. The index.dat as a hidden attribute. The desktop.ini has both a system and hidden attribute. So to view them you need to use the dir /a:s command and the attrib -s or attrib -h commands. You cannot delete them easily because of this; the file names are tedious to type out and you cannot delete the whole Content.IE5 directory with the rd command if it has files in it. This does not apply to other browsers that do not use the IE core. There are no index.dat or other hidden or system folders created by Mozilla or Firefox, for example. The cache folder can be deleted readily in Windows Explorer or with a batch file. 2. How to delete the IE6 cache completely2.1. DOSIf your Windows XP uses FAT or FAT32 then you can delete the whole Content.IE5 folder in DOS using a Win9x boot floppy disc.
2.2. WindowsThe simplest way is to delete the same folder from another user account. Log on to another account, go to the specific user folder in Documents and Settings, not the one you are currently logged on. If you don't have another user account, go to Safe Mode and logon to the root Administrator account. Open the subfolders and see what is there. You can just delete the contents of the index.dat and the four subfolders leaving the file and folders there but it is quicker to delete the whole Content.IE5 folder. On next reboot Windows will recreate it. A clean index.dat file is 32KB in size. You can also delete the same folder from another Windows XP installation; if the original installation is NTFS then the other must also be NTFS (see the example above in Fig. 1). You should use Shift + Delete (which does not store it in the Recycle Bin) or clear the Recycle Bin afterwards to avoid easy recovery. Normally this would be sufficient. If you wish to go further you can use an erase programme. I've found that it is possible to use a cmd script in Windows to delete the Content.IE5 folder including the index.dat file if explorer.exe is closed first. So the script has to do this (by using taskkill, built-in in Windows XP but not in older versions). I will post the script after further testing.
2.3. Microsoft Windows PEIf your Windows XP uses FAT32 or NTFS then you can delete the whole Content.IE5 folder using Windows PE offline. Windows PE is a new tool to replace DOS for system installation and maintenance (see my article on Windows PE).
2.4. Third party programmesSome internet cleanup programmes can delete the cache in the same user account because they can bypass the special Windows file attributes. Because you can readily do it yourself with the above methods there is no real need for them. ERD Commander 2005 works similarly to Windows PE and can do this.
Reference
Copyright © 2003-2005 by Kilian. All my articles including graphics are provided "as is" without warranties of any kind. I hereby disclaim all warranties with regard to the information provided. In no event shall I be liable for any damage of any kind whatsoever resulting from the information. The articles are provided in good faith and after some degree of verification but they may contain technical or typographical errors. Links to other web resources may be changed at any time and are beyond the control of the author. Articles may be added, removed, edited or improved at any time. No support is provided by the author. All the products mentioned are trademarks of their respective companies. This is not an official support page for Internet Explorer or other products mentioned. All the products mentioned are trademarks of their companies. Edit the registry at your own risk and back up first. Created 2003; updated 13 Nov 2005 |
||