Heliacal Risings and Settings
Definition: [Ancient Astrological Concepts] [Astrological Viewpoints] The heliacal rising of a star occurs on the day of the year when the star can be seen just before the dawn. Heliacal means 'near the Sun', from the Greek for Sun, Helios. On the day of helical rising the star glimmers near the eastern horizon a minute or two before the Sun's light drown out the stars. The next day it will be visible in the night sky for several minutes longer before dawn arrives.
The heliacal setting of a star occurs on the western horizon and marks the day when the star can be seen just above that horizon after dusk. On the next day the star will have already have set a few minutes before dusk, and will not be visible in the night sky until the day of its heliacal rising returns once more. For example, at the latitude of Babylon the star we now call Sirius would have not been seen in the night sky for about 65 days each year.

Heliacal risings and settings, in the eastern and western sky at dawn. The rising diagram shows the same star on the day of its rising, and it position the day before and the day after. |
Further Information: This attribute of the stars is caused by the fact that they set almost Four Minutes Earlier each night than the previous night, and hence they rise about four minutes earlier at dusk. Heliacal risings were very important to the calendars of ancient civilizations, as they provided the celestial ways of watching the passing cycle of the year. The ancient Babylonians included dates of Heliacal risings and Heliacal Node Stars on the Mul.Apin tablets, and were aware of the Four Minutes Earlier star setting each night. [see specifically Mul.Apin CIII Lines 49-50]. Heliacal risings have also been used for calendars in many other global civilisations. Both risings and settings and the time between feature prominently in the pre-classical Greek work, Hesiod's Works and Days. The Egyptians are said to have used the heliacal rising of Sirius to mark the start of their year, and the Nile flood season. Like Hesiod, Australian aborigines and Native North Americans used the risings of the Pleiades star cluster in Taurus to mark the times for agricultural and hunting activities. |
|
Reality: Heliacal risings and settings are a View Point illusion. The rising and setting of stars is an optical illusion brought about by the spin of the Earth about its own axis. That the stars appear to rise and set Four Minutes Earlier each night and that stars have heliacal risings are both artifacts of the Earth's orbit around the Sun. The drawing shows two helical risings six months apart. The risings are depicted by black arrows which show which stars are coming into view on the western horizon, just as the Sun sets, i.e. just as the spin of the Earth removes the Sun from view for your part of the planet. Six months later the Earth is on the opposite side of the Sun and the black arrow indicating your Viewpoint along the western horizon points to a completely different set of stars. The Four Minutes Earlier 'rising' is just a smaller version of the six monthly difference in stars. Because the Earth moves on in one day approximately one degree in its orbit, the stars you see heliacally rising next day are slightly different, and yesterday's heliacally rising star has already been 'up' for four minutes. |
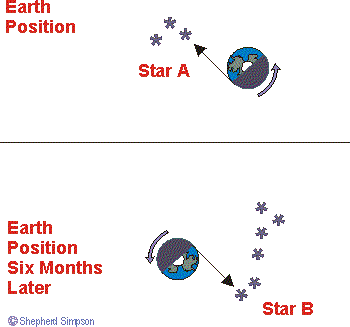
View of the solar system from above the plane of the Ecliptic. The black arrow shows the stars visible on the at sunset. The larger blue arrow indicates the Earth's orbit. The small blue arrow indicates the Earth's spin. |
© Dr Shepherd Simpson, Galactic Astrologer
The Galactic Astrologer
Do you want to know more about Galactic Astrology ?
Then enter the Galactic Zodiac
See the new Astrological Index for the meaning of other astrological words and phrases