Principal | Gráficos 3D | Gráficos 2D | Fractales | Math | Códigos | Tutoriales | Links
La convergencia lenta del método de Euler y lo restringido de su región de estabilidad absoluta nos lleva a considerar métodos de orden de convergencia mayor, un ejemplo es el llamado método Runge-Kutta de orden cuatro definido por las fórmulas:
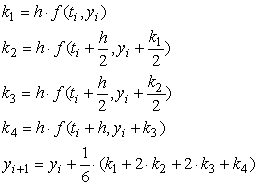
La exactitud del metodo de Runge-Kutta es mucho mayor que el de Euler.
En este ejemplo vamos a resolver la ecuacion diferencial :
![]()
mediante el metodo de Runge-Kutta con n=20, en el intervalo [0, 1].

/*
dy/dt = 1.0 - t + 4.0*y
y(0.0) = 1.0
*/
#include <GL/glut.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <stdio.h>
#include <math.h>
#define MAXPUNTOS 20
double y[MAXPUNTOS+1];
double t[MAXPUNTOS+1];
double f(double t, double y)
{
return (1.0 - t+ 4.0*y);
}
//solucion exacta de la ecuacion diferencial
double exacta(double t)
{
return (t/4.0 - 3.0/16.0 + (19.0/16.0)*exp(4.0*t));
}
void RK4(double tinicial, double tfinal, double yinicial, int n)
{
double k1, k2, k3, k4;
double h;
int i;
h=(tfinal-tinicial)/n;
t[0]=tinicial;
y[0]=yinicial;
for (i=0; i<n; i++)
{
k1=h*f(t[i], y[i]);
k2=h*f(t[i]+h/2.0, y[i]+k1/2.0);
k3=h*f(t[i]+h/2.0, y[i]+k2/2.0);
k4=h*f(t[i]+h, y[i]+k3);
y[i+1]=y[i]+(1.0/6.0)*(k1 + 2.0*k2 + 2.0*k3+ k4);
t[i+1]=t[i] + h;
}
}
void init(void)
{
RK4(0.0, 1.0, 1.0, MAXPUNTOS);
}
void display(void)
{
int i;
glClear(GL_COLOR_BUFFER_BIT);
glMatrixMode( GL_MODELVIEW_MATRIX );
glLoadIdentity();
//grafica de la solucion exacta en color Verde
glColor3f(0.0,1.0,0.0);
glBegin(GL_LINE_STRIP);
for (i=0; i<MAXPUNTOS; i++)
glVertex2f(t[i], exacta(t[i]));
glEnd();
//grafica de la solucion numerica en color Blanco
glColor3f(1.0,1.0,1.0);
glBegin(GL_LINE_STRIP);
for (i=0; i<MAXPUNTOS; i++)
glVertex2f(t[i], y[i]);
glEnd();
glFlush ();
}
void reshape (int w, int h)
{
if (!h)
return;
glViewport(0, 0, w, h);
glMatrixMode(GL_PROJECTION);
glLoadIdentity();
gluOrtho2D(0.0, 1.0, 0.0, 40.0);
glMatrixMode(GL_MODELVIEW);
glLoadIdentity();
}
void keyboard(unsigned char key, int x, int y)
{
switch (key)
{
case 27: exit(0);
break;
}
}
int main(int argc, char** argv)
{
glutInit(&argc, argv);
glutInitDisplayMode (GLUT_SINGLE | GLUT_RGB);
glutInitWindowSize (350, 350);
glutInitWindowPosition (0, 0);
glutCreateWindow ("Metodo de Runge-Kutta");
init ();
glutDisplayFunc(display);
glutReshapeFunc(reshape);
glutKeyboardFunc(keyboard);
glutMainLoop();
return 0;
}
|
valcoey@hotmail.com
Ramiro Alcocer, 2001
Principal | Gráficos 3D | Gráficos 2D | Fractales | Math | Códigos | Tutoriales | Links