El Problema de los Tres Cuerpos por Herling Gonzalez Alvarez
El Problema de los Tres Cuerpos es uno de los mas viejos problemas sin
resolver de la Fisica Clasica, primero formulado por Newton, su enunciado
es muy simple: Dada la masa de mi, posicion xi,
y velocidad vi de tres cuerpos (i=0,1,2) para t=0, determinar
su posicion en funcion del tiempo. No obstante, el sistema al ser
caotico, no tiene una solucion general, solo puede obtenerse aproximaciones
por medio de metodos numericos a la solucion.
Escribi este programa para resolver de manera numerica de Problema de
N-Cuerpos, el codigo en particular resuelve el "Problema de Tres
Cuerpos", confine mi atencion al movimiento en un plano (2D), y adapte
una atraccion gravitacional del tipo "softened":
![]()
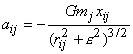
donde ai es la aceleracion total de la particula
i, aij es la aceleracion parcial de la
particula i, debido a la particula j, definimos a xij
= xi - xj, y r =
|xij|, el parametro ![]() suaviza
la ley del inverso-cuadrado para pequeñas separaciones de las masas, tomo
G = 1.
suaviza
la ley del inverso-cuadrado para pequeñas separaciones de las masas, tomo
G = 1.
Ante cualquier duda mi mail es el siguiente:
email: gherling@lycos.com
El programa
Este programa usa el metodo Predictor-Corrector para obtener los resultados
numericos de la simulacion y OpenGL para visualizarla y me limite a tres
cuerpos. Se pueden obtener una gran variedad de "orbitas", variando las
condiciones iniciales me refiero a la masa, la posicion, la velocidad
de cada uno de los tres cuerpos, a continuacion algunos ejemplos con su
respectiva salida grafica en todos los casos tome N = 3:
double eps=0.1,G=1.0;
double a=0.97000436, b=0.24308753;
double c=0.466203685,d=0.43236573;
double x[N]={-a, a, 0.0};
double y[N]={ b, -b, 0.0};
double vx[N]={-c, -c, 2*c};
double vy[N]={-d, -d, 2*d};
double m[N]={1.0, 1.0, 1.0};
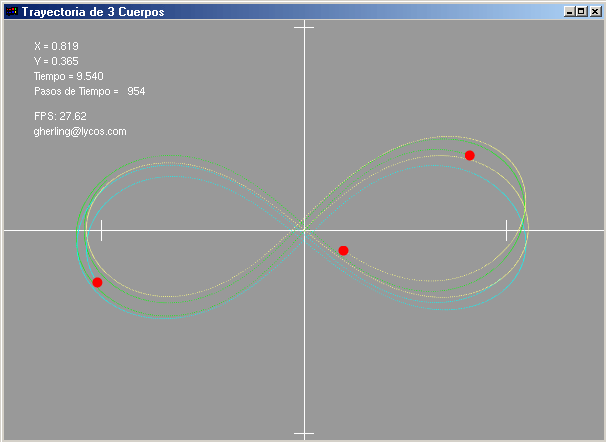
double eps=0.5,G=1.0;
double V=0.8;
double x[N]={-0.16666666666, 0.0, 0.16666666666};
double y[N]={0.866025403785, 0.0, -0.866025403785};
double vx[N]={-V, 0.0, V};
double vy[N]={-V, 0.0, V};
double m[N]={0.5, 10.0, 0.5};

double eps=0.2,G=1.0;
double V=0.5;
double x[N]={0.16666666666, 0.0, -0.16666666666};
double y[N]={0.866025403785, 0.0, -0.866025403785};
double vx[N]={V, 0.0, -V};
double vy[N]={-V, 0.0, V};
double m[N]={1.1, 10.0, 1.0};
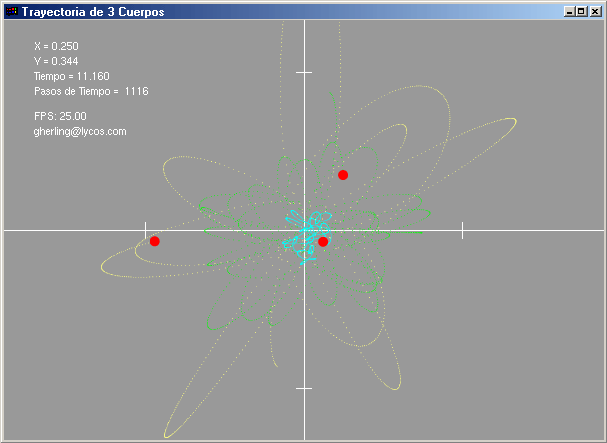
double eps=0.2,G=10.0;
double V=pow(3,-0.25);
double x[N]={1.0, -0.5, -0.5};
double y[N]={0.0, 0.866025403785, -0.866025403785};
double vx[N]={0.0,-0.866025403785*V, 0.866025403785*V};
double vy[N]={V,-0.5*V, -0.5*V};
double m[N]={1.0, 1.0, 1.0};

El Codigo Fuente
El codigo fue compilado con VisualC++ 6.0, las librerias OpenGL y GLUT
Codigo Fuente (6 kb)
Ejecutable (56 kb)
//
//NbodyGL.cpp
//trayectorias 2D para 3 cuerpos
//Herling Gonzalez Alvarez
//Copyright 2002
//gherling@lycos.com
//
#include<iostream.h>
#include<fstream.h>
#include<stdio.h>
#include<stdlib.h>
#include<string.h>
#include<math.h>
#include<GL/glut.h>
#ifndef M_PI
#define M_PI 3.141592653589793238E0
#endif
const int N=3;
int w,h,k,np=0;
int frame=0, times=0, timebase=0;
int moving, startx, starty;
const char *stick[]={"2","4","6","8","10"};
static char label[100];
double fps;
double theta=90.0,rho=90.0,distancia=10.0,xc=10.0,yc=10.0,zc=10.0;
double t=0,dt=0.01,tout=10;
//**************************************************************
double eps=0.1,G=1.0;
double a=0.97000436, b=0.24308753;
double c=0.466203685,d=0.43236573;
double x[N]={-a, a, 0.0};
double y[N]={ b, -b, 0.0};
double vx[N]={-c, -c, 2*c};
double vy[N]={-d, -d, 2*d};
double m[N]={1.0, 1.0, 1.0};
/*
double eps=0.5,G=1.0;
double V=0.8;
double x[N]={-0.16666666666, 0.0, 0.16666666666};
double y[N]={0.866025403785, 0.0, -0.866025403785};
double vx[N]={-V, 0.0, V};
double vy[N]={-V, 0.0, V};
double m[N]={0.5, 10.0, 0.5};
*/
/*
double eps=0.2,G=1.0;
double V=0.5;
double x[N]={0.16666666666, 0.0, -0.16666666666};
double y[N]={0.866025403785, 0.0, -0.866025403785};
double vx[N]={V, 0.0, -V};
double vy[N]={-V, 0.0, V};
double m[N]={1.1, 10.0, 1.0};
*/
/*
double eps=0.2,G=10.0;
double V=pow(3,-0.25);
double x[N]={1.0, -0.5, -0.5};
double y[N]={0.0, 0.866025403785, -0.866025403785};
double vx[N]={0.0,-0.866025403785*V, 0.866025403785*V};
double vy[N]={V,-0.5*V, -0.5*V};
double m[N]={1.0, 1.0, 1.0};
*/
//**************************************************************
double Ax[N], Ay[N], Ax1[N], Ay1[N],E=0.0;
struct _nodo{
double x, y;
_nodo *next;
_nodo() : next(0) {} //constructor
};
_nodo *nodos0=NULL;
_nodo *nodos1=NULL;
_nodo *nodos2=NULL;
void acel(double [], double []);
void renderScene(void);
void drawString (char*);
void Axis(void);
void init(void);
void changeSize(int, int);
void setOrthographicProjection(void);
void resetPerspectiveProjection(void);
void keyboard_1(unsigned char, int, int );
void keyboard_2(int, int, int);
void viewCam(double, double);
void mouse(int, int, int, int);
void motion( int, int);
void idle(void);
void body(void);
void drawLines(void);
void viewConsole();
void drawLines()
{
glColor3f(0.0, 1.0, 0.0);
glPointSize(1.0);
glBegin(GL_POINTS);
for (_nodo *curr0 = nodos0; curr0; curr0 = curr0->next)
glVertex2f(curr0->x, curr0->y);
glEnd();
glColor3f(0.0, 1.0, 1.0);
glPointSize(1.0);
glBegin(GL_POINTS);
for (_nodo *curr1 = nodos1; curr1; curr1 = curr1->next)
glVertex2f(curr1->x, curr1->y);
glEnd();
glColor3f(1.0, 1.0, 0.5);
glPointSize(1.0);
glBegin(GL_POINTS);
for (_nodo *curr2 = nodos2; curr2; curr2 = curr2->next)
glVertex2f(curr2->x, curr2->y);
glEnd();
}
void body(){
int i;
acel(x,y);
for(i=0;i<N;i++){
Ax1[i]=Ax[i];
Ay1[i]=Ay[i];
}
for(i=0;i<N;i++){
/* Predictor: */
x[i]+= dt*vx[i]+0.5*Ax1[i]*dt*dt;
y[i]+= dt*vy[i]+0.5*Ay1[i]*dt*dt;
vx[i]+= dt*Ax1[i];
vy[i]+= dt*Ay1[i];
}
acel(x,y);
for(i=0;i<N;i++){
/* Corrector: */
vx[i]+= 0.5*dt*(Ax[i]-Ax1[i]);
vy[i]+= 0.5*dt*(Ay[i]-Ay1[i]);
}
glPointSize(10.0);
glColor3f(1.0,0.0,0.0);
glBegin(GL_POINTS);
for(i=0;i<N;i++){
glVertex3f(x[i],y[i],0.0);
}
glEnd();
}
void renderScene(){
glClear(GL_COLOR_BUFFER_BIT | GL_DEPTH_BUFFER_BIT);
// Guarda la matriz actual en un stack
glPushMatrix();
glLineWidth(0.1);
Axis();
//---------------------------------------------------------------
_nodo *npt0 = new _nodo;
_nodo *npt1 = new _nodo;
_nodo *npt2 = new _nodo;
npt0->x = x[0];
npt0->y = y[0];
npt0->next=nodos0;
nodos0 = npt0;
npt1->x = x[1];
npt1->y = y[1];
npt1->next=nodos1;
nodos1 = npt1;
npt2->x = x[2];
npt2->y = y[2];
npt2->next=nodos2;
nodos2 = npt2;
drawLines();
body();
np+=1;
//---------------------------------------------------------------
glPopMatrix(); // Recupera la matriz guardada en el stack
//---- INTERFACE ORTOGRAFICA ---->
setOrthographicProjection();
glPushMatrix();
glLoadIdentity();
glColor3f(1.0,1.0,1.0);
sprintf (label, "X = %4.3f",x[0]);
glRasterPos2f (30,30.0);
drawString (label);
sprintf (label, "Y = %4.3f",y[0]);
glRasterPos2f (30,45.0);
drawString (label);
sprintf (label, "Tiempo = %4.3f",t);
glRasterPos2f (30,60.0);
drawString (label);
sprintf (label, "Pasos de Tiempo = %5d",np);
glRasterPos2f (30,75.0);
drawString (label);
sprintf(label,"FPS: %5.2f",fps);
glRasterPos2f(30.0,100.0);
drawString (label);
sprintf(label,"gherling@lycos.com");
glRasterPos2f(30.0,115.0);
drawString (label);
glPopMatrix();
resetPerspectiveProjection();
//----- INTERFACE ORTOGRAFICA ----<
glutSwapBuffers();
}
void drawString (char *s){
unsigned int i;
for (i = 0; i < strlen (s); i++)
glutBitmapCharacter (GLUT_BITMAP_HELVETICA_10, s[i]);
}
void init(){
glClearColor (0.6,0.6,0.6,0.0);
// glEnable(GL_LINE_SMOOTH);
glEnable(GL_BLEND);
glEnable(GL_POINT_SMOOTH);
glBlendFunc(GL_SRC_ALPHA, GL_ONE_MINUS_SRC_ALPHA);
// glHint(GL_LINE_SMOOTH_HINT,GL_DONT_CARE);
}
void changeSize(int w1, int h1)
{
if(h1 == 0) h1 = 1;
w = w1;
h = h1;
glViewport(0, 0, w, h); // Se va a usar toda la ventana para
// mostrar gráficos.
glMatrixMode(GL_PROJECTION);// Activamos la matriz de proyeccion.
glLoadIdentity(); // reseteamos la matrix de
// projection (stack=1).
gluPerspective(45, // Ángulo de visión.
(float)w/(float)h, // Razón entre el largo y el ancho,
// para calcular la perspectiva.
0.0001, // Cuan cerca se puede ver.
1000); // Cuan lejos se puede ver.
glMatrixMode(GL_MODELVIEW); // Escogemos la matriz de vista
glLoadIdentity();
gluLookAt(xc,yc,zc, // Desde donde miramos.
0.0, 0.0, 0.0, // Hacia donde miramos.
// x[0], y[0], 0.0, // Hacia donde miramos.
0.0, 1.0, 0.0); // Que eje es el que esta hacia arriba
}
void setOrthographicProjection()
{
glMatrixMode(GL_PROJECTION);
glPushMatrix();
glLoadIdentity();
gluOrtho2D(0, w, 0, h);
glScalef(1, -1, 1);
glTranslatef(0, -h, 0);
glMatrixMode(GL_MODELVIEW);
}
void resetPerspectiveProjection()
{
glMatrixMode(GL_PROJECTION);
glPopMatrix();
glMatrixMode(GL_MODELVIEW);
}
void keyboard_1(unsigned char key, int x, int y)
{
switch (key){
case 27 : exit(0); break;
case 'f': glutFullScreen();break;
case 'w': glutReshapeWindow(600,420);
glutPositionWindow(320,320);break;
case '-': distancia += 1.0; break;
case '+': distancia -= 1.0; break;
}
}
void keyboard_2(int key, int x, int y)
{
switch (key) {
case GLUT_KEY_LEFT : theta += 1.0;break;
case GLUT_KEY_RIGHT : theta -= 1.0;break;
case GLUT_KEY_UP : rho -= 1.0;break;
case GLUT_KEY_DOWN : rho += 1.0;break;
}
}
void viewCam(double theta, double rho)
{
xc = distancia*cos(theta*M_PI/180.0)*sin(rho*M_PI/180.0);
zc = distancia*sin(theta*M_PI/180.0)*sin(rho*M_PI/180.0);
yc = distancia*cos(rho*M_PI/180.0);
glLoadIdentity();
gluLookAt(xc,yc,zc,
0.0, 0.0, 0.0, // Hacia donde miramos.
// x[0], y[0], 0.0, // Hacia donde miramos.
0.0, 1.0, 0.0);
}
void mouse ( int button, int state, int x, int y )
{
if ( button == GLUT_LEFT_BUTTON && state == GLUT_DOWN )
{
moving = 2; //=1
startx = x;
starty = y;
}
if ( button == GLUT_LEFT_BUTTON && state == GLUT_UP )
moving = 0;
if ( button == GLUT_RIGHT_BUTTON && state == GLUT_DOWN )
{
moving = 2;
starty = y;
}
if ( button == GLUT_RIGHT_BUTTON && state == GLUT_UP )
moving = 0;
}
void motion ( int x, int y )
{
if ( moving == 1 )
{
theta = theta + (x - startx)*0.5;
rho = rho + (y - starty)*0.5;
startx = x;
starty = y;
glutPostRedisplay();
}
if ( moving == 2 )
{
distancia = distancia + (y - starty) * 0.1;
starty = y;
glutPostRedisplay ( );
}
}
void idle()
{
t += dt;
if(theta > 360 || theta < -360) theta=0.0;
if(rho > 360 || rho < -360) rho=0.0;
viewCam(theta,rho);
frame++;
times=glutGet(GLUT_ELAPSED_TIME);
if (times - timebase > 1000)
{
fps=frame*1000.0/(times-timebase);
timebase = times;
frame = 0;
}
glutPostRedisplay();
}
void acel(double x[], double y[])
{
double sumax,sumay;
for(int i=0;i<N;i++){
sumax=0,sumay=0;
for(int j=0;j<N;j++){
if(i!=j){
sumax += -G*(x[i]-x[j])*m[j]
/pow((x[i]-x[j])*(x[i]-x[j])+
(y[i]-y[j])*(y[i]-y[j])+eps*eps,1.5);
sumay += -G*(y[i]-y[j])*m[j]
/pow((x[i]-x[j])*(x[i]-x[j])+
(y[i]-y[j])*(y[i]-y[j])+eps*eps,1.5);
}
}
Ax[i]=sumax;
Ay[i]=sumay;
}
}
void Axis(){
int ix,iy,wW=5,wH=5;
int step = 1;
double hashWidth = 0.05;
glColor3f(1., 1., 1.);
// Hash marks for the y - axis
for (iy = step; iy < wH; iy += step){
glBegin(GL_LINES);
glVertex2f(-hashWidth, iy);
glVertex2f(hashWidth, iy);
glVertex2f(-hashWidth, -iy);
glVertex2f(hashWidth, -iy);
glEnd();
}
// Hash marks for the x - axis
for (ix = step; ix < wW; ix += step){
glBegin(GL_LINES);
glVertex2f(ix, hashWidth);
glVertex2f(ix, -hashWidth);
glVertex2f(-ix, hashWidth);
glVertex2f(-ix, -hashWidth);
glEnd();
}
glColor3f(1, 1, 1);
glBegin(GL_LINES);
// x - axis
glVertex2f(-wW, 0);
glVertex2f( wW, 0);
// y - axis
glVertex2f(0, wH);
glVertex2f(0, -wH);
glEnd();
}
void viewConsole()
{
cout<< "--------------------------------"<<endl;
cout<< " Trayectoria de 3 Cuerpos "<<endl;
cout<< "--------------------------------"<<endl;
cout<< " gherling@lycos.com "<<endl;
cout<< "--------------------------------"<<endl;
cout<< " TECLAS y Mouse: "<<endl;
cout<< "--------------------------------"<<endl;
cout<< "UP,LEFT,RIGHT,DOWN para mover la vista"<<endl;
cout<< "+ y - se aleja o se acerca."<<endl;
cout<< " "<<endl;
}
int main(int argc, char **argv)
{
viewConsole();
glutInit(&argc, argv);
glutInitDisplayMode(GLUT_DEPTH | GLUT_DOUBLE | GLUT_RGBA);
glutInitWindowPosition(0,0);
glutInitWindowSize(600,420);
glutCreateWindow("Trayectoria de 3 Cuerpos");
init();
glutReshapeFunc(changeSize);
glutMouseFunc(mouse);
glutMotionFunc(motion);
glutKeyboardFunc(keyboard_1);
glutSpecialFunc(keyboard_2);
glutIdleFunc(idle);
glutDisplayFunc(renderScene);
glutMainLoop();
return 0;
}