Module
12: RAS and Dial-Up Networking
- Windows NT RAS uses standard Public Switched
Telephone Networks (PSTN).
- Advantage is worldwide availability.
|
Client/server
|
Configuration
|
| Client for Win95
or Windows NT |
PAD converts serially transmitted data into
X.25 packets, or vice versa to make communication possible between
the client and the X.25 network. |
| Server and client
(NT only) |
A direct connection
to the X.25 network can be made through a X.25 smart cards. This is
a hardware card with a PAD embedded in it and acts like a modem |
- This offers much faster communication than
PSTN. ISDN lines must be installed at both the server and the remote side
and an ISDN adapter must be installed in both.
- (For more background and comparison b/w modems
and ISDN adapters, see 399 Study Guide.
| Point-to Point Tunneling Protocol (PPTP) |
- RAS Servers are usually accessed by modem,
ISDN card or an X.25 PAD.
- BUT They can also be accessed indirectly
via Internet with PPTP.PPTP is a networking technology that supports multi-protocol
virtual private networks (VPNs).
- This support enables remote users to gain secure
access to corporate networks across the Internet.
- Using PPTP, first a connection to the Internet
is established and the a connection to the RAS server on the Internet is established.
PPTP Advantages
|
Advantage
|
Description
|
| Lower transmission
costs |
- If local access is available through
ISP, access to the remote network is less expensive than a long distance
telephone call
|
| Lower hardware costs |
- RAS Server needs only a connection to
the Internet
- Not necessary for RAS Server to have
multiple modems, ISDN or X.25 cards.
|
| Lower administration
costs |
- a PPTP network can be managed and
secured from a single RAS server
|
| Better Security |
- PPTP provides security through data encryption
and works with:
- Data sent by means of PPTP consists of
encapsulated PPP packets.
|
How PPTP works
Comparing PPTP and Other WAN Protocols
- PSTN, ISDN, or X25 a remote access client
establishes a PPP connection with RAS server over switched network.
- After connection is established, PPP packets
are sent over the switched connection to RAS server for routing to the destination
LAN.
- PPTP uses a transport protocol such as TCP/IP
to send PPP packets to the RAS server over virtual WAN. Resulting benefit
is saving in transmission costs by using Internet rather than long distance
dial-up connections.
PPTP Access Over the Internet
There are two methods:
|
Method for connecting
to RAS server
|
Considerations
|
| Direct connection
to Internet |
- Client must have PPTP driver
- RAS server must PPTP enabled adapter
to establish tunnel via Internet
|
| Connection through
ISP |
- If an ISP provides the connection,
and the ISP's Point of Presence (POP) supports PPTP, then
PPTP does not have to be installed on the client.
- The client establishes a connection to the ISP and calls the NT
RAS server to establish the PPTP tunnel.
|
LAN Protocols:
Windows NT RAS supports these protocols and therefore these networks by using
the PPP remote access standard.
| Protocol: |
NetBEUI |
TCP/IP |
IPX |
| Network: |
Microsoft-based |
UNIX |
Novell Netware |
- Clients running Windows NT RAS can also
connect to existing SLIP-based remote access servers (UNIX).
| SLIP (Serial LIne Internet Protocol) |
- addresses TCP/IP connections made over serial
lines.
- supported by DUN.
- gives access to Internet services.
Limitations
- Requires static IP address for client, therefore
cannot utilize DHCP or WINS
- Relies on text-based logon sessions and requires
a scripting system to automate logon process.
- Supports only
TCP/IP
- transmits authentication passwords as CLEAR
TEXT therefore, is NOT very secure.
- Windows NT RAS does not have a SLIP server
component, so it CANNOT be used as a SLIP server ð
so you can't call into an NT RAS server using SLIP
| PPP: Point to Point Protocol |
- Designed to enhance SLIP
- Set of industry standard framing and authentication
protocols that enable RAS clients and servers to interoperate in multivendor
network.
- Supports AppleTalk, DECnet, OSI, TCP/IP, and
IPX.
- PPP support
- enables computers running Windows
NT to dial in to remote networks through any server that complies with PPP
standard and
- enables computers running NT
Server to receive calls from, and provide access to, other vendors’
remote access software.
- The PPP architecture enables clients to load any combination of NetBEUI,
TCP/IP, and IPX. Applications written to the Windows Sockets (WinSock),
NetBIOS, or IPX interface can be run on a remote computer running Windows
NT Workstation.
Netware Points:
- Windows NT RAS clients that have both the IPX interface and CSNW installed
can connect directly to and access NetWare servers.
- If RAS client does not have IPX and CSNW installed, it can still access
a NetWare server if GSNW is installed on a RAS server. The RAS server then
functions as a gateway to a NetWare server.
Windows NT RAS can act as a
- NetBIOS Gateway
- NT RAS includes a NetBIOS gateway that enables remote clients to access
NetBIOS resources, such as file and print services, on a network.
- This enables clients running NetBEUI to access remote servers regardless
of which protocol is installed on the remote sever.
- The NetBIOS gateway does this by translating the NetBEUI packets into
IPX or TCP/IP formats that can be understood by remote servers.
| Aspects of Windows NT RAS Security
to validate remote client access to network |
- Integrated Domain Security
- Windows NT Server provides organization wide
security using a single network logon model (also for RAS users).
- This means easier administration and remote
clients have same privileges as when they are in the office.
- To connect to a RAS server, user must have
RAS dial-in permission (is authenticated) and a valid Windows NT user account.
- Clients must first be authenticated by RAS before they can log on to NT
network.
- Encrypted Authentication and
Logon Process
- By default, all authentication and logon information is encrypted when
transmitted over RAS.
- However, it is possible to allow any authentication method, including
clear text.
- In addition, it is possible to configure RAS and Dial-Up Networking so
that all data that passes between a client and server is encrypted.
- Auditing
- if auditing is enabled, RAS can generate
audit information on remote connections including authentication and logon.
- Intermediary Security Hosts
- This is a third-party intermediary security
host between DUN client and RAS server. Users must type password before
establishing a connection with RAS Server.
- Callback Security
- When callback security is used, the server receives the call from the
client computer, disconnects the connection, and then calls the client back
either at a preset telephone number or at a number that was provided during
the initial call.
- This guarantees that the connection to the local network was made from
a trusted site, such a branch office.
- PPTP Filtering
- when using PPTP, the RAS server must have
a direct connection to the Internet and a company's corporate network.
- this could pose security risk, because access
to the network could be gained through RAS server.
- PPTP filtering can be used to help ensure
security on a corporate network.
- When PPTP filtering is enabled, all other
protocols other than PPTP are disabled on the selected network adapter.
- Enable PPTP Filtering in Advanced
IP Addressing in Microsoft TCP/IP Properties dialog box.
Windows NT Telephony API (TAPI):
- Provides a standard way for communication applications
to control telephony functions for data, fax, and voice calls.
- Virtualizes the telephone system by acting
as a device driver for a telephone network.
- Manages all signaling between computer and
telephone network (establishing, answering and terminating calls).
- Can also include supplementary functions such
as hold, transfer, conference, and call park found in PBX and ISDN.
TAPI Settings:
Basic TAPI settings are set up when a TAPI-aware
program (DUN) is run for the first time. If is has not been run before, the
TAPI configuration will be automatically installed when DUN is installed.
- Location
in Windows NT DUN it is a set of information that TAPI uses to analyze telephone
numbers in international format and to determine the correct sequence of numbers
to be dialed. Can be named anything that can help the user remember them.
Information includes:
- Area or city code
- Country code
- Outside line access (for local and long distance
calls)
- Preferred calling card
- Creates the sequence of numbers to be dialed
for a particular calling card.
- Number is stored in scrambled form and will
not be displayed after it is entered.
- Multiple calling cards can be defined.
- Drivers (TAPI Service Providers
= TSPs)
- Software components that control TAPI hardware
(PBX, voice mail card)
- Are installed with TAPI hardware except TAPI
driver for modems (unimodem.tsp) is automatically installed with
NT
- ALL TSP's run in same memory space, so malfunctioning
TSP can affect others.
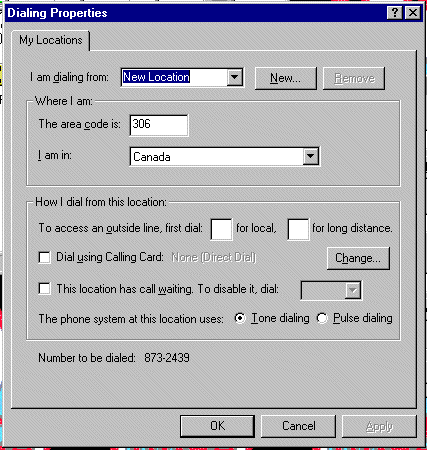
Configuring a TAPI Location
Done through Dialing Properties dialog
box and then choose My Locations tab:
|
Option
|
Use this option to
|
| I am dialing
from <list box> + New button |
Current location
+ additional |
| The area
code is |
Enter area code
for TAPI location |
| I am in |
Current country
name |
| To access
an outside line |
|
| Dialing using
calling card |
|
| Change button |
Change calling
card used for this location |
| This location
has call waiting. To disable it, dial |
turned of when
dialing from a computer |
| The phone
system at this location uses |
Tone or pulse |
- RAS can be installed either during or after
installation of Windows NT 4.0.
- If Remote Access to the Network is selected
during setup both RAS and DUN will be installed.
- For both, the following information is required:
- Modem model
- Type of communication port used for RAS
- Whether computer is used for dial in, dial
out, or both
- Protocols to be used
- Modem setting (baud rate)
- Security setting (including callback)
Note:
- Windows NT Server 4.0 supports
256 RAS connections
- NT Workstation supports only
1.
|
- Specify hardware that RAS will use including
modem type and port.
- This is done by Remote Access Setup dialog
box in the Services tab of the Network program in Control
Panel
Click Remote Access Service and
click Properties. Following configuration options:
|
Option
|
Use this option to
|
| Add |
Make port available
to RAS and install
- modem,
- X.25 PAD,
- or a VPN for PPTP
|
| Remove |
Make port unavailable
to RAS |
| Configure |
Change RAS settings
for the port such as intended usage
- Dial out only à
enables DUN clients to use port to initiate calls
- Receive call only àenables
RAS server to receive calls from DUN clients on port
- Dial out and receive calls à
enables RAS server to use port
for DUN client or server function
|
| Clone |
Copy same modem
setup from one port to another |
| Network |
Configure network protocol,
multilink, and encryption settings 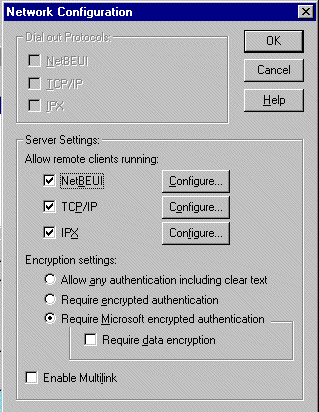
- Dial out Protocols
select dial out protocols
- Server Settings
- select and configure the protocols
that the RAS server can use for servicing remote clients
- Encryption Settings
- select authentication level ranging
from clear text to Microsoft encrypted authentication;
- if Require Microsoft encrypted
authentication is selected, the Require data encryption
can also be selected
- Enable multilink
- enable DUN PPP multilink protocol
(client and server must have it enabled)
|
| Configuring a RAS Server
to Use NetBEUI |
- If NetBEUI protocol has been installed, the
RAS Setup program enables NetBEUI and the NetBIOS gateway by default.
- RAS servers use NetBEUI to provide remote clients
with access to small workgroups or department sized LANs.
- To configure a RAS server to use NetBEUI, in
the Network Configuration dialog box, select NetBEUI checkbox,
click Configure. RAS Server NetBEUI Configuration dialog box appears.
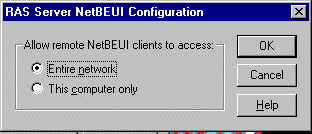
Use it to enable remote NetBEUI clients to gain
access to:
- Entire network
- This computer only
| Configuring a RAS Server
to Use TCP/IP |
Same as with NetBEUI but now you
select TCP/IP and click Configure.
The RAS Server TCP/IP Configuration dialog box
appears.
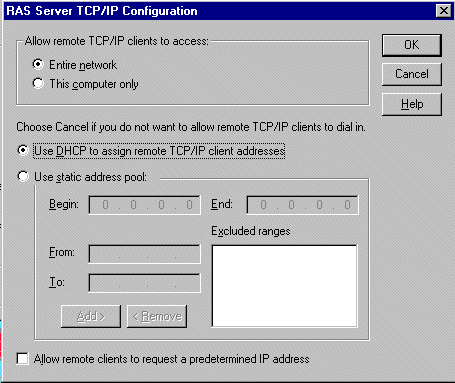
|
Option
|
Use this option to
|
| Allow remote
TCP/IP clients to access |
To entire network
or This computer only |
| Use DHCP to
assign remote TCP/IP client addresses |
- Use DHCP server to dynamically assign
an IP address to the client.
- DUN clients require an IP address
on a TCP/IP network
|
| Use static address
pool |
- This uses a pre-assigned pool of
IP addresses
- Configure IP address range; designate
beginning and ending values.
- Add and Remove buttons can be used
to exclude any IP addresses
|
| Allow remote
clients to request a predetermined IP address |
|
| Configuring a RAS Server
to Use IPX |
- The RAS Server IPX Configuration dialog box
appear after clicking IPX and then Configure.
- DUN clients can gain access to NetWare server
file and print sharing resources through RAS servers that support IPX.
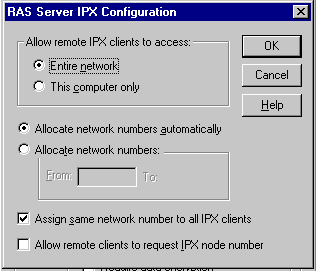
|
Option
|
Use this option to
|
| Allow remote
IPX clients to access |
To entire network
or This computer only |
| Allocate network
number automatically |
Assign network
numbers automatically to DUN clients |
| Allocate network
numbers |
Assign network
numbers manually to DUN clients |
| Assign same
network number to all IPX clients |
Assign a single
network number to all IPX clients |
| Allow remote
clients to request IPX node number |
Enable DUN clients
to request IPX node number |
| Installing Dial-Up Networking |
DUN is automatically installed during Windows
NT installation if Remote access to the network is selected during setup.
- Automatically installed on computers running
Windows NT Server/Workstation when RAS is installed.
- Manually installed by double clicking Dial-Up
Networking icon in My Computer.
| Configuring Phonebook
Entries |
- DUN clients store all of its configuration
data for a single connection in a phonebook file.
- Specific to individual user or shared among
all users on the computer (called a system phonebook). To create or edit phonebook
entries, access DUN through My Computer or by Start, Programs, Accessories.
- Configuration for a single connection is kept
in a phonebook file
Rasphone.pbk
- Use the New Phonebook Entry wizard to create
the first phonebook entry.
- Turning off the Wizard:
- After gaining experience with phonebook
entries, it may be more efficient to turn of the wizard by selecting the
I know all about phonebook entries and would rather edit the properties
directly check box.
- Turning the Wizard back on again
- To use the wizard again in My Computer,
double click Dial-Up Networking, click More and then click
User Preferences. Click Appearance tab and then Use Wizard
to create new phonebook entries and click OK. Next time a new phonebook
entry is created, the wizard will start.
| New Phonebook Entry Configuration |
To do this, in My Computer double click Dial-Up
Networking and then click New.
The New Phonebook Entry dialog box appears with
following configuration options:
| Basic Tab |
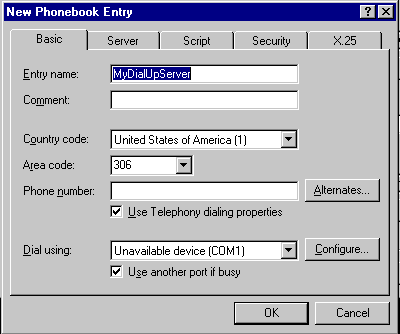 |
Use this tab to:
- To configure a name for the phonebook
entry
- To enter the telephone number, alternated
numbers, and to use Telephony dialing properties
- To specify and configure the device used
by phonebook entry
|
Server Tab
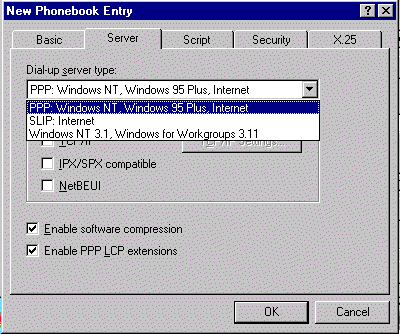
Use this tab to: To select and configure
remote access protocols (PPP, SLIP or earlier) and network protocols
Other options depend on server type but include
selecting network protocol and selecting software data compression
In addition, the following TCP/IP settings (Server
tab) may need to be configured by pressing the TCP/IP Settings buttons.
TCP/IP setting are only available for if you choose
PPP or SLIP in the Servers tab.
| PPP |
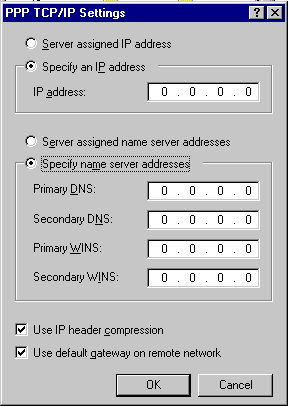 |
SLIP |
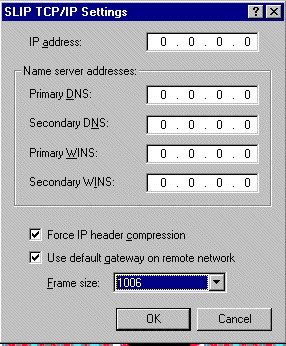 |
|
Option
|
Description
|
| IP address |
Automatically assigned
by dial-up server or manually configured on clients. |
| Name Server addresses |
Assign DNS and WINS
server addresses; assigned by DHCP server or manually configured |
| Use IP header compression |
Enable header compression
for low-speed serial links |
| Use default gateway
on remote network |
Select this if DUN
client is using network card to connect simultaneously to a LAN. When this
check box is selected, packets that cannot be routed on local network are
forwarded to default gateway on remote network |
| Script Tab: |
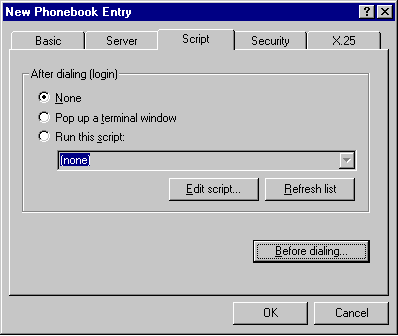 |
Use this tab to:
- To specify terminal window or script
file if manual intervention is required before or after dialing
|
Security Tab
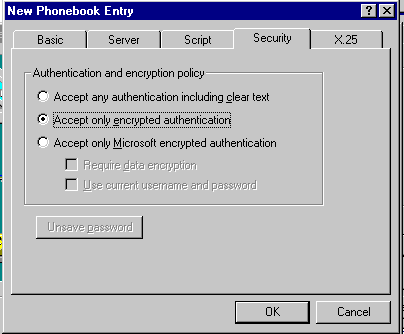
Use this tab to: To select level of authentication
and encryption
X.25 Tab
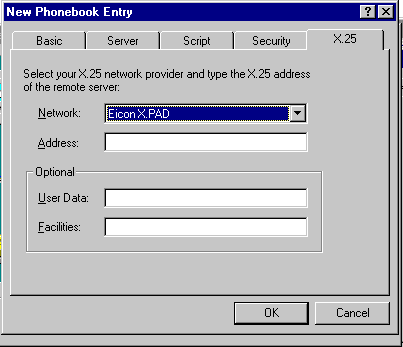
Use this tab to: To select X.25 network
provider To configure connectivity information
required by X.25 network provider
| Logging On Through Dial-Up
Networking |
- When DUN is installed users can select DUN
phonebook entry that they will use to log on.
- DUN establishes a connection to RAS server
so that domain controller can validate logon request.
Dial-Up Settings
These are configured using Logon Preferences
dialog box on DUN client (see table).
To access this box click More in Dial-Up Networking
dialog box, and then on More menu click Logon preferences.
| Dialing |
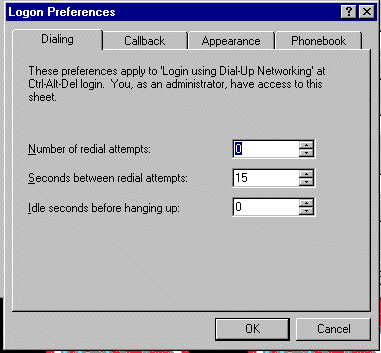
- Specify number of and interval between
redial attempts
- To set idle connection timeout period
|
| Callback |
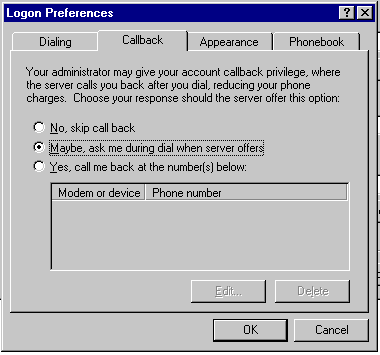
- Configure the server to disconnect and
to call the client back following authentication
|
| Appearance |
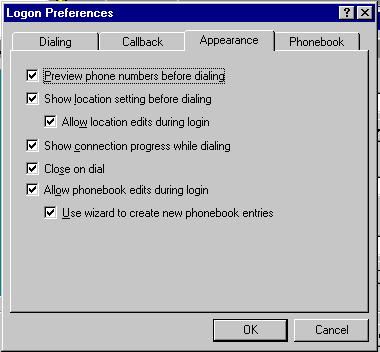
- Configure DUN interface that appears
during logon
|
| Phonebook |
- Specify system phonebook or an alternate
phonebook to be used during logon
|
- NT uses the same logon process for logging
on to a LAN directly or through DUN.
- A copy of a user profile is cached on the client
each time the user logs off.
- Configure Windows NT to use the locally-cached
profile through the User Profiles tab, which is accessible through
the System program in Control Panel.
| AutoDial (supported by Windows
NT 4.0 DUN) and AutoDial Mapping Database |
- The NT client maintains network addresses and
maps them to phonebook entries. This mapping allows automatic dialing when
a user references the network address from an application or from the command
line.
- The AutoDial database can include IP addresses,
Internet host names or NetBIOS names. Each address in the database is associated
with a set of entries. RAS can use these entries to dial from a particular
TAPI dialing location.
- The following table describes the situation
in which AutoDial automatically creates entries in its database.
|
Situation
|
AutoDial response
|
| Failure to connect
to a network address |
If there is
no entry for address in mapping database, and computer is not connected
to a network, AutoDial prompts the user to specify the information necessary
to establish a dial-up connection. If it is successful AutoDial stores
information in database |
| Connection to
a network through RAS |
When a user
connects to a network address, AutoDial creates an entry in the database.
The entry maps the network address to the phonebook entry that was used
to establish the RAS connection |
AutoDial tracks all DUN connections so that clients
can be automatically reconnected. AutoDial attempts to make a reconnection in
following situations:
- If a client is disconnected from the network
and it is running an application that references a network connection.
- If a client is connected to a network AutoDial
attempts to create network connection for addresses it has previously learned.
| Enabling and Disabling AutoDial |
- in User Preferences dialog box for a
phonebook entry
- to enable, in Dial-Up Networking dialog
box, and then in Phonebook entry to dial list, select an entry. Click
More and then click User Preferences. Click Dialing tab,
and then in the Enable auto-dial by location list, select each location
listed.
- to disable, on Dialing tab, click to
clear each location listed in the Enable auto-dial by location list.
AutoDial:
- only works when Remote Access Autodial Manager
is running
- not supported by Windows 95 and Windows NT
versions earlier than 4.0
- does not support IPX connections;
only supports TCP/IP and NetBEUI
Logs and the Like
There are 4 ways to log RAS related activities:
- MODEMLOG.TXT
- records modem activities
- file is in the NT root directory
- DEVICE.LOG
- enabled only thru registry
- records ???
- stored in \winnt_root\system32\RAS
- Event Viewer
- is used to view the system log
- Contains events for all internal services
and drivers
- Many RAS events are entered in the system
log.
- PPP.LOG
- can be created to capture debugging information
related to PPP authentication problems
- stored in \winnt_root\system32\RAS
- Enabled by setting registry value to 1
of
Authentication Problems over RAS
- try to change the authentication settings for
that client.
- Try lowest option on each side (i.e. allowing
any authentication including clear text option)
- Start increasing to determine the highest level
that can be used between the two systems.
Dial-Up Networking Monitor
- Can be accessed through Dial-Up Monitor program
in Control Panel. It shows status of a session that is in progress.
- Shows duration of a call, amount of data transmitted
and received, number of errors
- Shows which lines are in use for multilink
sessions
- can configure the user interface for sounds
and for location of the status indicator
Multilink and Callback
- put simply, CALLBACK doesn't WORK with Multilink
- If a client uses multilink enabled phonebook
entry to call a server that is configured to call the user back, when callback
is made it will be to one of the multilink devices. For one user account
there is only one callback number to be stored. So no multilink functionality.
- If the link is made using ISDN with two channels
that have the same phone number, the Multilink WILL work with callback.
AutoDial Occurs During Logon
- during logon, when NT Explorer initializes,
any persistent network connections or desktop shortcuts that reference network
locations will cause AutoDial to attempt to make a connection.
- Avoid this by disabling AutoDial or remove
shortcuts.
RAS Configuration Files
Modem.inf
- contains info describing each modem supported by RAS
- used to configure initializations strings, compression, flow control,
connect strings..and so on.
- RAS supports over 200 modems
- can modify this file to add entries for modems not currently supported
by RAS ( But generally, modification is not recommended)
Pad.inf
- contains info describing each PAD supported by RAS
- don't modify except to add new PAD not currently supported
Switch.inf
- contains info describing each intermediately device supported by RAS (e.g..
security hosts)
- don't modify except to add new device not currently supported
Serial.ini
- contains info describing the currently configured COM port(s), including
info on device attached to the port(s)
- the file is created and maintained by the RAS Setup program accessed through
Control Panel | Network
- Don't edit manually: use Control Panel
Personal Phonebook
- each user can have a personal phone book
- this provides additional security because it's not available to all users
- created using the user's logon name with a .pbk extension
- it's stored in \winnt_root\system32\RAS
| How RAS Authenticates User Connections |
There are three options shown:
| Client Side |
Server Side |
 |
 |
| Accept any authentication including clear text |
- least secure
- intended to support any third party dial-in clients that employ the Password
Authentication Protocol (PAP)
Password Authentication Protocol (PAP)
| Accept only encrypted authentication |
Authentication protocol options here include:
RSA Message Digest 5 (MD5) Challenge Handshake Authentication (CHAP)
- this is used on a RAS client ONLY
- NT supports MD5 for outbound dialing allowing Windows NT clients to connect
with virtually all third-party servers
- Because RSA MD5 requires a clear text (no encryption) password at the server,
NT does not support MD5 for inbound dialing
NOTE
- if you use a packet analyzer to watch the traffic, you can read user names
and passwords
- for security purposes, the CHAP server sends a random challenge to client,
which changes every time.
- client encrypts the challenge with user's password and sends it back to
the server
SPAP Shiva Password Authentication Protocol
- a version of PAP implemented by Shiva
- NT supports it to allow interoperability with Shiva LAN clients
Data Encryption Standard (DES)
- designed by the National Bureau of Standards
- supported for backward compatibility with LAN Manager-based system
RSA Message Digest 4 (MD4) or MS-CHAP
- the only clients that currently support the MS-CHAP authentication method
are the Windows NT and the Windows NT RAS clients. That is:
- NT Server
- NT Workstation
- Win 95 (?)
- When connecting, these two systems will ALWAYS use MS-CHAP when negotiating
passwords
- enabled on NT Server by default
- most secure encryption algorithm
- all data can also be encrypted
- either the client or the server can require data encryption to be negotiate
| Accept Only Microsoft encrypted authentication |
- This forces the use of MS-CHAP for authentication
 Comments and suggestions? E-mail me at
grantwilson21@yahoo.com
Comments and suggestions? E-mail me at
grantwilson21@yahoo.com
I'm sorry, but I can't answer specific network-related, or exam-related questions. |
| Last Updated: August 6, 2001 |
Grant Wilson, Edmonton, AB
Canada |